Fetal hematopoietic stem cells express MFG-E8 during mouse embryogenesis
- PMID: 26206421
- PMCID: PMC4525298
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2015.42
Fetal hematopoietic stem cells express MFG-E8 during mouse embryogenesis
Abstract
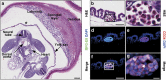
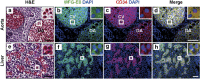
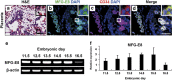
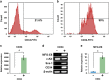
The milk fat globule-EGF-factor 8 protein (MFG-E8) has been identified in various tissues, where it has an important role in intercellular interactions, cellular migration, and neovascularization. Previous studies showed that MFG-E8 is expressed in different cell types under normal and pathophysiological conditions, but its expression in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) during hematopoiesis has not been reported. In the present study, we investigated MFG-E8 expression in multiple hematopoietic tissues at different stages of mouse embryogenesis. Using immunohistochemistry, we showed that MFG-E8 was specifically expressed in CD34(+) HSCs at all hematopoietic sites, including the yolk sac, aorta-gonad-mesonephros region, placenta and fetal liver, during embryogenesis. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting and polymerase chain reaction analyses demonstrated that CD34(+) cells, purified from the fetal liver, expressed additional HSC markers, c-Kit and Sca-1, and that these CD34(+) cells, but not CD34(-) cells, highly expressed MFG-E8. We also found that MFG-E8 was not expressed in HSCs in adult mouse bone marrow, and that its expression was confined to F4/80(+) macrophages. Together, this study demonstrates, for the first time, that MFG-8 is expressed in fetal HSC populations, and that MFG-E8 may have a role in embryonic hematopoiesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adhesion activity of fetal gonadal cells to EGF and discoidin domains of milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 (MFG-E8), a secreted integrin-binding protein which is transiently expressed in mouse early gonadogenesis.Anat Embryol (Berl). 2005 Jul;209(6):485-94. doi: 10.1007/s00429-005-0463-0. Epub 2005 May 13. Anat Embryol (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15891907
-
Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8): a novel protein in the mammalian endometrium with putative roles in implantation and placentation.Placenta. 2012 Oct;33(10):795-802. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2012.06.015. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Placenta. 2012. PMID: 22770563
-
Re-evaluation of milk-fat globule EGF-factor VIII (MFG-E8) as an intrinsic component of the mouse milk-fat globule membrane.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76(11):2055-60. doi: 10.1271/bbb.120412. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23132565
-
Embryonic hematopoiesis.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2013 Dec;51(4):226-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2013. PMID: 24041595 Review.
-
Identification of MFG-E8 as a novel therapeutic target for diseases.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 Nov;17(11):1275-85. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.829455. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23972256 Review.
Cited by
-
The Possible Importance of β3 Integrins for Leukemogenesis and Chemoresistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 15;19(1):251. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010251. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29342970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Vascular Aging: Mechanisms and Its Role in Age-related Diseases.Aging Dis. 2017 Jul 21;8(4):486-505. doi: 10.14336/AD.2017.0507. eCollection 2017 Jul. Aging Dis. 2017. PMID: 28840062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Modulation of Fetal Liver Hematopoietic Stem Cell Mobilization into Fetal Bone Marrow in Mice.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Dec 15;2020:8885154. doi: 10.1155/2020/8885154. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 33381191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Levels of MFG-E8 Confer a Good Prognosis in Prostate and Renal Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 4;14(11):2790. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112790. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carrascosa C, Obula RG, Missiaglia E, Lehr HA, Delorenzi M, Frattini M, et al. MFG-E8/lactadherin regulates cyclins D1/D3 expression and enhances the tumorigenic potential of mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2012;31:1521–1532. - PubMed
-
- Ensslin MA, Shur BD. Identification of mouse sperm SED1, a bimotif EGF repeat and discoidin-domain protein involved in sperm-egg binding. Cell. 2003;114:405–417. - PubMed
-
- Ye H, Li B, Subramanian V, Choi BH, Liang Y, Harikishore A, et al. NMR solution structure of C2 domain of MFG-E8 and insights into its molecular recognition with phosphatidylserine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1828:1083–1093. - PubMed
-
- Andersen MH, Berglund L, Rasmussen JT, Petersen TE. Bovine PAS-6/7 binds alpha v beta 5 integrins and anionic phospholipids through two domains. Biochemistry. 1997;36:5441–5446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

