Selective Retinoic Acid Receptor γ Agonists Promote Repair of Injured Skeletal Muscle in Mouse
- PMID: 26205250
- PMCID: PMC4597269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.05.007
Selective Retinoic Acid Receptor γ Agonists Promote Repair of Injured Skeletal Muscle in Mouse
Abstract
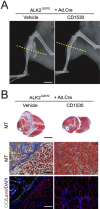
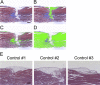
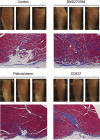
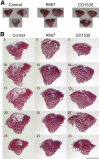
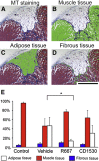
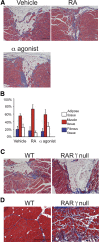
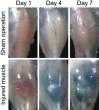
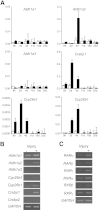
Retinoic acid signaling regulates several biological events, including myogenesis. We previously found that retinoic acid receptor γ (RARγ) agonist blocks heterotopic ossification, a pathological bone formation that mostly occurs in the skeletal muscle. Interestingly, RARγ agonist also weakened deterioration of muscle architecture adjacent to the heterotopic ossification lesion, suggesting that RARγ agonist may oppose skeletal muscle damage. To test this hypothesis, we generated a critical defect in the tibialis anterior muscle of 7-week-old mice with a cautery, treated them with RARγ agonist or vehicle corn oil, and examined the effects of RARγ agonist on muscle repair. The muscle defects were partially repaired with newly regenerating muscle cells, but also filled with adipose and fibrous scar tissue in both RARγ-treated and control groups. The fibrous or adipose area was smaller in RARγ agonist-treated mice than in the control. In addition, muscle repair was remarkably delayed in RARγ-null mice in both critical defect and cardiotoxin injury models. Furthermore, we found a rapid increase in retinoid signaling in lacerated muscle, as monitored by retinoid signaling reporter mice. Together, our results indicate that endogenous RARγ signaling is involved in muscle repair and that selective RARγ agonists may be beneficial to promote repair in various types of muscle injuries.
Copyright © 2015 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RARγ is a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Jun;150:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 20. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25800721
-
A molecular basis for retinoic acid-induced axial truncation.Dev Biol. 1999 Jan 1;205(1):33-48. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.9110. Dev Biol. 1999. PMID: 9882496
-
Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of retinoic acid receptor γ function promotes endochondral bone formation.J Orthop Res. 2017 May;35(5):1096-1105. doi: 10.1002/jor.23347. Epub 2016 Jul 22. J Orthop Res. 2017. PMID: 27325507 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid Agonists in the Targeting of Heterotopic Ossification.Cells. 2021 Nov 19;10(11):3245. doi: 10.3390/cells10113245. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antagonizing RARγ Drives Necroptosis of Cancer Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 27;23(9):4814. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094814. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563205 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of All-trans Retinoic Acid on Panniculus Carnosus Muscle Regeneration in Fetal Mouse Wound Healing.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022 Sep 28;10(9):e4533. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004533. eCollection 2022 Sep. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022. PMID: 36187276 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SW033291 on the myogenesis of muscle-derived stem cells and muscle regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Feb 21;11(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-1574-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32085799 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Cardiotoxin-Induced Muscle Injury Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 2;23(21):13380. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Administration of a selective retinoic acid receptor-γ agonist improves neuromuscular strength in a rodent model of volumetric muscle loss.J Exp Orthop. 2021 Aug 12;8(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s40634-021-00378-3. J Exp Orthop. 2021. PMID: 34383202 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid maintains human skeletal muscle progenitor cells in an immature state.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 May;74(10):1923-1936. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2445-1. Epub 2016 Dec 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28025671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Close G.L., Kayani A., Vasilaki A., McArdle A. Skeletal muscle damage with exercise and aging. Sports Med. 2005;35:413–427. - PubMed
-
- Aarimaa V., Rantanen J., Heikkila J., Helttula I., Orava S. Rupture of the pectoralis major muscle. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32:1256–1262. - PubMed
-
- McCarthy E.F., Sundaram M. Heterotopic ossification: a review. Skeletal Radiol. 2005;34:609–619. - PubMed
-
- Rantanen J., Thorsson O., Wollmer P., Hurme T., Kalimo H. Effects of therapeutic ultrasound on the regeneration of skeletal myofibers after experimental muscle injury. Am J Sports Med. 1999;27:54–59. - PubMed
-
- Almekinders L.C. Anti-inflammatory treatment of muscular injuries in sport: an update of recent studies. Sports Med. 1999;28:383–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

