Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with decreased immunosuppressive potential of the IgG glycome
- PMID: 26200652
- PMCID: PMC4626261
- DOI: 10.1002/art.39273
Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with decreased immunosuppressive potential of the IgG glycome
Abstract
Objective: Glycans attached to the Fc portion of IgG are important modulators of IgG effector functions. Interindividual differences in IgG glycome composition are large and they associate strongly with different inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. IKZF1, HLA-DQ2A/B, and BACH2 genetic loci that affect IgG glycome composition show pleiotropy with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), indicating a potentially causative role of aberrant IgG glycosylation in SLE. We undertook this large multicenter case-control study to determine whether SLE is associated with altered IgG glycosylation.
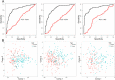
Methods: Using ultra-performance liquid chromatography analysis of released glycans, we analyzed the composition of the IgG glycome in 261 SLE patients and 247 matched controls of Latin American Mestizo origin (the discovery cohort) and in 2 independent replication cohorts of different ethnicity (108 SLE patients and 193 controls from Trinidad, and 106 SLE patients and 105 controls from China).
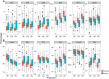
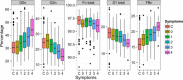
Results: Multiple statistically significant differences in IgG glycome composition were observed between patients and controls. The most significant changes included decreased galactosylation and sialylation of IgG (which regulate proinflammatory and antiinflammatory actions of IgG) as well as decreased core fucose and increased bisecting N-acetylglucosamine (which affect antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity).
Conclusion: The IgG glycome in SLE patients is significantly altered in a way that decreases immunosuppressive action of circulating immunoglobulins. The magnitude of observed changes is associated with the intensity of the disease, indicating that aberrant IgG glycome composition or changes in IgG glycosylation may be an important molecular mechanism in SLE.
© 2015 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between immunoglobulin G N-glycosylation and lupus nephritis in female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 21;14:1257906. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1257906. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809087 Free PMC article.
-
IgG N-glycome changes during the course of severe COVID-19: An observational study.EBioMedicine. 2022 Jul;81:104101. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104101. Epub 2022 Jun 27. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35773089 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the causal relationships between human IgG N-glycosylation and 12 common diseases associated with changes in the IgG N-glycome.Hum Mol Genet. 2022 May 19;31(10):1545-1559. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab335. Hum Mol Genet. 2022. PMID: 34791244
-
Sweet but dangerous - the role of immunoglobulin G glycosylation in autoimmunity and inflammation.Lupus. 2016 Jul;25(8):934-42. doi: 10.1177/0961203316640368. Lupus. 2016. PMID: 27252272 Review.
-
The Role of B Cell and T Cell Glycosylation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):863. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010863. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunoglobulin G N-glycan, inflammation and type 2 diabetes in East Asian and European populations: a Mendelian randomization study.Mol Med. 2022 Sep 14;28(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00543-z. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36104772 Free PMC article.
-
ST6Gal1 in plasma is dispensable for IgG sialylation.Glycobiology. 2022 Aug 18;32(9):803-813. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwac039. Glycobiology. 2022. PMID: 35746897 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Longitudinal Changes in Immunoglobulin G N-Glycosylation Associate with Therapy Response in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 30;23(15):8473. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158473. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955616 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring of immunoglobulin N- and O-glycosylation in health and disease.Glycobiology. 2020 Mar 20;30(4):226-240. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwz048. Glycobiology. 2020. PMID: 31281930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between immunoglobulin G N-glycosylation and lupus nephritis in female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 21;14:1257906. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1257906. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mihai S, Nimmerjahn F. The role of Fc receptors and complement in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 2013;12:657–60. - PubMed
-
- Gornik O, Pavic T, Lauc G. Alternative glycosylation modulates function of IgG and other proteins: implications on evolution and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012;1820:1318–26. - PubMed
-
- Malhotra R, Wormald MR, Rudd PM, Fischer PB, Dwek RA, Sim RB. Glycosylation changes of IgG associated with rheumatoid arthritis can activate complement via the mannose‐binding protein. Nat Med 1995;1:237–43. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara C, Stuart F, Sondermann P, Brunker P, Umana P. The carbohydrate at FcγRIIIa Asn‐162: an element required for high affinity binding to non‐fucosylated IgG glycoforms. J Biol Chem 2006;281:5032–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

