Functional Integration of mRNA Translational Control Programs
- PMID: 26197342
- PMCID: PMC4598765
- DOI: 10.3390/biom5031580
Functional Integration of mRNA Translational Control Programs
Abstract
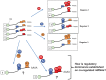
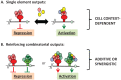
Regulated mRNA translation plays a key role in control of cell cycle progression in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including in the self-renewal and survival of stem cells and cancer stem cells. While targeting mRNA translation presents an attractive strategy for control of aberrant cell cycle progression, mRNA translation is an underdeveloped therapeutic target. Regulated mRNAs are typically controlled through interaction with multiple RNA binding proteins (RBPs) but the mechanisms by which the functions of distinct RBPs bound to a common target mRNA are coordinated are poorly understood. The challenge now is to gain insight into these mechanisms of coordination and to identify the molecular mediators that integrate multiple, often conflicting, inputs. A first step includes the identification of altered mRNA ribonucleoprotein complex components that assemble on mRNAs bound by multiple, distinct RBPs compared to those recruited by individual RBPs. This review builds upon our knowledge of combinatorial control of mRNA translation during the maturation of oocytes from Xenopus laevis, to address molecular strategies that may mediate RBP diplomacy and conflict resolution for coordinated control of mRNA translational output. Continued study of regulated ribonucleoprotein complex dynamics promises valuable new insights into mRNA translational control and may suggest novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of disease.
Keywords: CPEB; Musashi; RNA-binding protein; combinatorial control; mRNA translation; mRNP; regulation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Context-dependent regulation of Musashi-mediated mRNA translation and cell cycle regulation.Cell Cycle. 2011 Jan 1;10(1):39-44. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.1.14388. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21191181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of turnover and translation regulatory RNA-binding protein expression through binding to cognate mRNAs.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(18):6265-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00500-07. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17620417 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro translation of mRNAs that are in their native ribonucleoprotein complexes.Biochem J. 2015 Nov 15;472(1):111-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150772. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 26349537
-
Translational control by CPEB: a means to the end.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jul;2(7):521-9. doi: 10.1038/35080081. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11433366 Review.
-
RNA-binding protein-mediated post-transcriptional controls of gene expression: integration of molecular mechanisms at the 3' end of mRNAs?Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Jun 15;89(4):431-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24735612
Cited by
-
CPEB2 Is Necessary for Proper Porcine Meiotic Maturation and Embryonic Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 12;19(10):3138. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103138. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30322039 Free PMC article.
-
CNOT6 regulates a novel pattern of mRNA deadenylation during oocyte meiotic maturation.Sci Rep. 2018 May 1;8(1):6812. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25187-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29717177 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA Metabolism in Cardiac Development and Disease: Life After Transcription.Physiol Rev. 2020 Apr 1;100(2):673-694. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00007.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Physiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 31751167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of embryonic RNA granules that act as sites of mRNA translation after changing their physical properties.iScience. 2022 May 5;25(6):104344. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104344. eCollection 2022 Jun 17. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35620421 Free PMC article.
-
Musashi Exerts Control of Gonadotrope Target mRNA Translation During the Mouse Estrous Cycle.Endocrinology. 2023 Aug 1;164(9):bqad113. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad113. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37477898 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

