Experimental Evidence Shows Salubrinal, an eIF2α Dephosphorylation Inhibitor, Reduces Xenotoxicant-Induced Cellular Damage
- PMID: 26193263
- PMCID: PMC4519949
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160716275
Experimental Evidence Shows Salubrinal, an eIF2α Dephosphorylation Inhibitor, Reduces Xenotoxicant-Induced Cellular Damage
Abstract
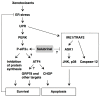
Accumulating evidence indicates that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and the subsequent unfolded protein response (UPR) are involved in the pathogenesis of not only the protein misfolding disorders such as certain neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases, but also in the cytotoxicity of environmental pollutants, industrial chemicals, and drugs. Thus, the modulation of ER stress signaling pathways is an important issue for protection against cellular damage induced by xenotoxicants. The substance salubrinal has been shown to prevent dephosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2α). The phosphorylation of eIF2α appears to be cytoprotective during ER stress, because inhibition of the translation initiation activity of eIF2α reduces global protein synthesis. In addition, the expression of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), a transcription factor that induces the expression of UPR target genes, is up-regulated through alternative translation. This review shows that salubrinal can protect cells from the damage induced by a wide range of xenotoxicants, including environmental pollutants and drugs. The canonical and other possible mechanisms of cytoprotection by salubrinal from xenotoxicant-induced ER stress are also discussed.
Keywords: ATF4; ER stress; apoptosis; cytoprotection; drugs; eIF2α; environmental pollutants; salubrinal; xenotoxicants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of salubrinal on cadmium-induced apoptosis in HK-2 human renal proximal tubular cells.Arch Toxicol. 2012 Jan;86(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s00204-011-0742-x. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Arch Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 21809093
-
Sevoflurane-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Contributes to Neuroapoptosis and BACE-1 Expression in the Developing Brain: The Role of eIF2α.Neurotox Res. 2017 Feb;31(2):218-229. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9671-z. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 27682474
-
Enhanced signaling downstream of ribonucleic Acid-activated protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase potentiates lipotoxic endoplasmic reticulum stress in human islets.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Mar;95(3):1442-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-2322. Epub 2010 Jan 15. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20080856
-
Targeting phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor-2α to treat human disease.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;106:75-106. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396456-4.00005-5. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22340715 Review.
-
A new pharmacology--drugging stressed folding pathways.Trends Mol Med. 2005 Aug;11(8):347-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2005.06.011. Trends Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16005683 Review.
Cited by
-
Translation Regulation by eIF2α Phosphorylation and mTORC1 Signaling Pathways in Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 26;21(15):5301. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155301. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32722591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer-Specific Induction of Cell Death by Silver Nanoparticles by Combined Treatment with Proteotoxic Stress Response Inhibitors.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;14(19):1564. doi: 10.3390/nano14191564. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39404291 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular docking studies of salubrinal and its analogs as inhibitors of the GADD34:PP1 enzyme.ADMET DMPK. 2019 Apr 5;7(2):140-150. doi: 10.5599/admet.632. eCollection 2019. ADMET DMPK. 2019. PMID: 35350543 Free PMC article.
-
Salubrinal enhances eIF2α phosphorylation and improves fertility in a mouse model of Classic Galactosemia.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Nov 1;1865(11):165516. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.07.010. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 31362041 Free PMC article.
-
Panorama of the Intracellular Molecular Concert Orchestrated by Actinoporins, Pore-Forming Toxins from Sea Anemones.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Aug 13;13(8):567. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080567. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

