Inhibition of smoothened decreases proliferation of synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 26189371
- PMCID: PMC5301154
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2015.67
Inhibition of smoothened decreases proliferation of synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
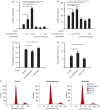
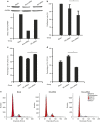
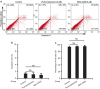
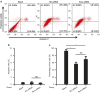
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) contribute to synovial hyperplasia in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Smoothened (Smo) is a key component of sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling and contributes to tumor cell proliferation. The objective of this study was to investigate the role of Smo in RA synoviocyte proliferation. FLSs were isolated from RA synovium. Shh signaling was studied using a Smo antagonist (GDC-0449) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting the Smo gene in FLSs. Cell proliferation was quantified by using kit-8 assay and cell cycle distribution and apoptosis were evaluated by flow cytometry. Cell cycle-related genes and proteins were detected by real-time PCR and western blot. FLSs treated with GDC-0449 or Smo-siRNA showed significantly decreased proliferation compared to controls (P < 0.05). Incubation with GDC-0449 or transfection with Smo-siRNA resulted in a significant increase of G1 phase cells compared to controls (P < 0.05). Cell cycle arrest was validated by the significant increase in cyclin D1 and E1 mRNA expression, decrease in cyclin-dependent kinase p21 mRNA expression in Smo-siRNA transfected cells (P < 0.05). Protein expression of cyclin D1 was also downregulated after Smo gene knockdown (P < 0.05). The results suggest that Shh signaling plays an important role in RA-FLSs proliferation in a Smo-dependent manner and may contribute to synovial hyperplasia. Targeting Shh signaling may help control joint damage in patients with RA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Smoothened Regulates Migration of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via Activation of Rho GTPase Signaling.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 15;8:159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00159. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28261216 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Mediates Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 5;9:2847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02847. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30568656 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6 inhibition mitigates the pro-inflammatory roles and proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Cytokine. 2017 May;93:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 12. Cytokine. 2017. PMID: 28506571
-
Involvement of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Apr 20;133(8):941-950. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000755. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020. PMID: 32187055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic alterations in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Epigenomics. 2017 Apr;9(4):479-492. doi: 10.2217/epi-2016-0151. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Epigenomics. 2017. PMID: 28322585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sonic Hedgehog Regulates Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via JNK Signaling.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 24;11:1300. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01300. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32670287 Free PMC article.
-
Smoothened Regulates Migration of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via Activation of Rho GTPase Signaling.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 15;8:159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00159. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28261216 Free PMC article.
-
Chemically modified small interfering RNA targeting Hedgehog signaling pathway for rheumatoid arthritis therapy.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Dec 12;31:88-104. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.12.008. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 36618268 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic Hedgehog Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via Rho/ROCK Signaling.J Immunol Res. 2022 Jun 22;2022:3423692. doi: 10.1155/2022/3423692. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35785032 Free PMC article.
-
A protocol for humanized synovitis mice model.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2019 Oct 15;8(5):47-52. eCollection 2019. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31777685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tak PP, Bresnihan B. The pathogenesis and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: advances from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis. Arthritis Rheum 2000; 43: 2619–2633. - PubMed
-
- Mor A, Abramson SB, Pillinger MH. The fibroblast-like synovial cell in rheumatoid arthritis: a key player in inflammation and joint destruction. Clin Immunol 2005; 115: 118–128. - PubMed
-
- Pap T, Nawrath M, Heinrich J, Bosse M, Baier A, Hummel KM et al. Cooperation of Ras- and c-Myc-dependent pathways in regulating the growth and invasiveness of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: 2794–2802. - PubMed
-
- Nasu K, Kohsaka H, Nonomura Y, Terada Y, Ito H, Hirokawa K et al. Adenoviral transfer of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor genes suppresses collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Immunol 2000; 165: 7246–7252. - PubMed
-
- Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young KE, Corden JL, Westphal H et al. Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature 1996; 383: 407–413. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

