Detection of gold nanorods uptake by macrophages using scattering analyses combined with diffusion reflection measurements as a potential tool for in vivo atherosclerosis tracking
- PMID: 26185445
- PMCID: PMC4501352
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S86615
Detection of gold nanorods uptake by macrophages using scattering analyses combined with diffusion reflection measurements as a potential tool for in vivo atherosclerosis tracking
Abstract
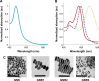
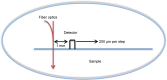
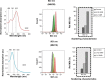
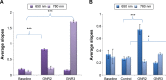
In this study, we report a potential noninvasive technique for the detection of vulnerable plaques using scatter analyses with flow cytometry (FCM) method combined with the diffusion reflection (DR) method. The atherosclerotic plaques are commonly divided into two major categories: stable and vulnerable. The vulnerable plaques are rich with inflammatory cells, mostly macrophages (MΦ), which release enzymes that break down collagen in the cap. The detection method is based on uptake of gold nanorods (GNR) by MΦ. The GNR have unique optical properties that enable their detection using the FCM method, based on their scattering properties, and using the DR method, based on their unique absorption properties. This work demonstrates that after GNR labeling of MΦ, 1) the FCM scatter values increased up to 3.7-fold with arbitrary intensity values increasing from 1,110 to 4,100 and 2) the DR slope changed from an average slope of 0.196 (MΦ only) to an average slope of 0.827 (MΦ labeled with GNR) (P<0.001 for both cases). The combination of FCM and DR measurements provides a potential novel, highly sensitive, and noninvasive method for the identification of atherosclerotic vulnerable plaques, aimed to develop a potential tool for in vivo tracking.
Keywords: flow cytometry; gold nanoparticles; macrophages; noninvasive detection; vulnerable plaques.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle uptake by macrophages in vulnerable plaques for atherosclerosis diagnosis.J Biophotonics. 2015 Nov;8(11-12):871-83. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201500114. Epub 2015 Jun 25. J Biophotonics. 2015. PMID: 26110589 Review.
-
Gold nanorods as absorption contrast agents for the noninvasive detection of arterial vascular disorders based on diffusion reflection measurements.Nano Lett. 2014 May 14;14(5):2681-7. doi: 10.1021/nl500573d. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Nano Lett. 2014. PMID: 24697682
-
In-vivo Tumor detection using diffusion reflection measurements of targeted gold nanorods - a quantitative study.J Biophotonics. 2012 Mar;5(3):263-73. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201100120. Epub 2012 Jan 11. J Biophotonics. 2012. PMID: 22234916
-
Subcutaneous gold nanorods [corrected] detection with diffusion reflection measurement.J Biomed Opt. 2013 Jun;18(6):61226. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.6.061226. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 23389735
-
Recent advances in analytical and bioanalysis applications of noble metal nanorods.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Nov;398(6):2451-69. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3937-8. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20644918 Review.
Cited by
-
Iterative optical technique for detecting anti-leishmania nanoparticles in mouse lesions.Biomed Opt Express. 2021 Jun 28;12(7):4496-4509. doi: 10.1364/BOE.425798. eCollection 2021 Jul 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 34457428 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Gold Nanorod Features for the Enhanced Performance of Plasmonic Nanocavity Arrays.ACS Omega. 2021 Oct 22;6(43):29071-29077. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04301. eCollection 2021 Nov 2. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34746596 Free PMC article.
-
The Scattering of Gold Nanorods Combined with Differential Uptake, Paving a New Detection Method for Macrophage Subtypes Using Flow Cytometery.Nano Lett. 2020 Nov 11;20(11):8360-8368. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03525. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Nano Lett. 2020. PMID: 33063518 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion Reflection Measurements of Antibodies Conjugated to Gold Nanoparticles as a Method to Identify Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Borders.Materials (Basel). 2020 Jan 17;13(2):447. doi: 10.3390/ma13020447. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31963462 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory Nanoparticle for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Vascular Diseases.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016 Jul 1;23(7):757-65. doi: 10.5551/jat.35113. Epub 2016 Apr 25. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016. PMID: 27108537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roifman I, Beck PL, Anderson TJ, Eisenberg MJ, Genest J. Chronic inflammatory diseases and cardiovascular risk: a systematic review. Can J Cardiol. 2011;27(2):174–182. - PubMed
-
- Melzer S, Ankri R, Fixler D, Tarnok A. Nanoparticle uptake by macrophages in vulnerable plaques a tool for atherosclerosis diagnosis. J Biophotonics. 2015;10:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Burgner DP, Sabin MA, Magnussen CG, et al. Early childhood hospitalisation with infection and subclinical atherosclerosis in adulthood: the cardiovascular risk in Young Finns Study. Atherosclerosis. 2015;239(2):496–502. - PubMed
-
- Weintraub HS. Identifying the vulnerable patient with rupture-prone plaque. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101(12):S3–S10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

