Changes in Mitochondrial Toxicity in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells During Four-Year Administration of Entecavir Monotherapy in Chinese Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 26176539
- PMCID: PMC4515935
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.892937
Changes in Mitochondrial Toxicity in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells During Four-Year Administration of Entecavir Monotherapy in Chinese Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess whether long-term entecavir monotherapy induces mitochondrial toxicity in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
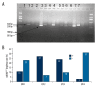
Material and methods: This was a prospective study in 34 antiviral treatment-naïve patients with CHB who received entecavir monotherapy and were followed up for 4 years. Blood samples were collected after 0, 2, 3, and 4 years of entecavir (ETC) monotherapy (ETC0, ETC2, ETC3, and ETC4, respectively). Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) contents were determined using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and mtDNA4977 depletions were detected using nested PCR. Levels of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA, alanine aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg), creatine kinase, urea nitrogen, and serum creatinine were recorded.
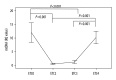
Results: mtDNA contents at ETC0 (9.6±6.3) and ETC4 (10.3±6.2) were markedly higher than at ETC2 (0.8±0.5, P<0.01) and ETC3 (1.3±0.9, P<0.01), but there were no differences between ETC2 and ETC3 or between ETC0 and ETC4. MtDNA4977 depletion appeared in 79.4% cases at ETC2 and in 70.6% at ETC3, which were much higher than at ETC0 (32.4%, P<0.01) and ETC4 (8.8%, P<0.01), but there were no differences in mtDNA4977 depletion ratio between ETC2 and ETC3, or between ETC0 and ETC4. mtDNA content was negatively correlated to mtDNA4977 depletion (partial regression coefficient of -4.555, P<0.001, R2=0.315). mtDNA content was positively correlated with age (partial regression coefficient of 0.131, P=0.045).
Conclusions: Results suggest that during 4-year entecavir monotherapy for CHB, the mtDNA contents initially decreased and then increased, while the mtDNA4977 depletion rates first increased and then decreased.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Entecavir treatment causes injury to the mitochondrial DNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2012 Oct;20(10):751-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2012.10.009. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23207335 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Efficacy of prolonged entecavir monotherapy in treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B patients exhibiting a partial virologic response to entecavir.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015 Mar;21(1):24-31. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2015.21.1.24. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25834799 Free PMC article.
-
A 24-week, parallel-group, open-label, randomized clinical trial comparing the early antiviral efficacy of telbivudine and entecavir in the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adult Chinese patients.Clin Ther. 2010 Apr;32(4):649-58. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.001. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20435234 Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of telbivudine and entecavir for chronic hepatitis B in real-world clinical practice.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012 Mar;67(3):696-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr495. Epub 2011 Dec 15. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22174039
-
Entecavir for the treatment of patients with hepatitis B virus-related decompensated cirrhosis.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013 Jul;14(10):1363-9. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2013.786701. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23557465 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial toxicity and body shape changes during nucleos(t)ide analogues administration in patients with chronic hepatitis B.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 6;10(1):2014. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58837-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32029790 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Brinkman K, ter Hofstede HJ, Burger DM, et al. Adverse effects of reverse transcriptase inhibitors: mitochondrial toxicity as common pathway. AIDS. 1998;12:1735–44. - PubMed
-
- Lewis W, Dalakas MC. Mitochondrial toxicity of antiviral drugs. Nat Med. 1995;1:417–22. - PubMed
-
- Kohler JJ, Hosseini SH. Subcellular renal proximal tubular mitochondrial toxicity with tenofovir treatment. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;755:267–77. - PubMed
-
- Caron-Debarle M, Lagathu C, Boccara F, et al. HIV-associated lipodystrophy: from fat injury to premature aging. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16:218–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

