Autophagy attenuates the catabolic effect during inflammatory conditions in nucleus pulposus cells, as sustained by NF-κB and JNK inhibition
- PMID: 26165348
- PMCID: PMC4533778
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2280
Autophagy attenuates the catabolic effect during inflammatory conditions in nucleus pulposus cells, as sustained by NF-κB and JNK inhibition
Abstract
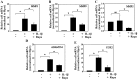
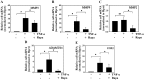
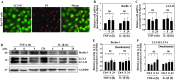
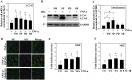
Proteoglycan degradation contributing to the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration is induced by inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor‑α (TNF‑α) and interleukin‑1β (IL‑1β). Cell autophagy exists in degenerative diseases, including osteoarthritis and intervertebral disc degeneration. However, the autophagy induced by TNF‑α and IL‑1β and the corresponding molecular mechanism appear to be cell‑type dependent. The effect and mechanism of autophagy regulated by TNF‑α and IL‑1β in IVDs remains unclear. Additionally, the impact of autophagy on the catabolic effect in inflammatory conditions also remains elusive. In the present study, autophagy activator and inhibitor were used to demonstrate the impact of autophagy on the catabolic effect induced by TNF‑α. A critical role of autophagy was identified in rat nucleus pulposus (NP) cells: Inhibition of autophagy suppresses, while activation of autophagy enhances, the catabolic effect of cytokines. Subsequently, the autophagy‑related gene expression in rat NP cells following TNF‑α and IL‑1β treatment was observed using immunofluorescence, quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis; however, no association was present. In addition, nuclear factor κB (NF‑κB), c‑Jun N‑terminal kinase (JNK), extracellular signal‑regulated kinases and p38 mitogen‑activated protein kinase inhibitors and TNF‑α were used to determine the molecular mechanism of autophagy during the inflammatory conditions, and only the NF‑κB and JNK inhibitor were found to enhance the autophagy of rat NP cells. Finally, IKKβ knockdown was used to further confirm the effect of the NF‑κB signal on human NP cells autophagy, and the data showed that IKKβ knockdown upregulated the autophagy of NP cells during inflammatory conditions.
Figures
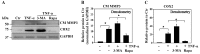
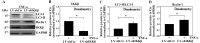
Similar articles
-
Prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain protein 2 controls NF-κB/p65 transactivation and enhances the catabolic effects of inflammatory cytokines on cells of the nucleus pulposus.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 13;290(11):7195-207. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.611483. Epub 2015 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25635047 Free PMC article.
-
Piperine mediates LPS induced inflammatory and catabolic effects in rat intervertebral disc.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 19;8(6):6203-13. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261497 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor α- and interleukin-1β-dependent induction of CCL3 expression by nucleus pulposus cells promotes macrophage migration through CCR1.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Mar;65(3):832-42. doi: 10.1002/art.37819. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23233369 Free PMC article.
-
Immune cascades in human intervertebral disc: the pros and cons.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 May 15;6(6):1009-14. Print 2013. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23696917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy: A double-edged sword in intervertebral disk degeneration.Clin Chim Acta. 2016 Jun 1;457:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2016.03.016. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Clin Chim Acta. 2016. PMID: 27018178 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction with small molecules in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration.Geroscience. 2021 Apr;43(2):517-537. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00341-1. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Geroscience. 2021. PMID: 33634362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR‑654‑5p inhibits autophagy by targeting ATG7 via mTOR signaling in intervertebral disc degeneration.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jun;23(6):444. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12083. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33846806 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Pathway in the Process of Cartilage Endplate Stem Cell Degeneration Induced by Tension Load.Global Spine J. 2023 Oct;13(8):2396-2408. doi: 10.1177/21925682221085226. Epub 2022 Apr 9. Global Spine J. 2023. PMID: 35400210 Free PMC article.
-
BMSC-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Modulating AKT/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy of Nucleus Pulposus Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Jul 9;2022:9896444. doi: 10.1155/2022/9896444. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. PMID: 35855812 Free PMC article.
-
The circadian rhythm in intervertebral disc degeneration: an autophagy connection.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Jan;52(1):31-40. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0372-6. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31983731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pockert AJ, Richardson SM, Le Maitre CL, Lyon M, Deakin JA, Buttle DJ, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA. Modified expression of the ADAMTS enzymes and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 3 during human intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:482–491. doi: 10.1002/art.24291. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

