New immunotherapies targeting the PD-1 pathway
- PMID: 26162965
- PMCID: PMC4562806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.06.005
New immunotherapies targeting the PD-1 pathway
Abstract
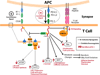
Ligands from the B7 family bind to receptors of the CD28 family, which regulate early T cell activation in lymphoid organs and control inflammation and autoimmunity in peripheral tissues. Programmed death-1 (PD-1), a member of the CD28 family, is an inhibitory receptor on T cells and is responsible for their dysfunction in infectious diseases and cancers. The complex mechanisms controlling the expression and signaling of PD-1 and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) are emerging. Recently completed and ongoing clinical trials that target these molecules have shown remarkable success by generating durable clinical responses in some cancer patients. In chronic viral infections, preclinical data reveal that targeting PD-1 and its ligands can improve T cell responses and virus clearance. There is also promise in stimulating this pathway for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
Keywords: PD-1; PD-L1; PD-L2; cancer; immunotherapy; viral infection.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and its ligands in pediatric cancer.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015 Feb;62(2):190-197. doi: 10.1002/pbc.25284. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25327979 Review.
-
[Anti-PD-1 antibody: basics and clinical application].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2013 Sep;40(9):1145-9. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2013. PMID: 24047772 Japanese.
-
Clinical evaluation of compounds targeting PD-1/PD-L1 pathway for cancer immunotherapy.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2015 Dec;21(6):451-67. doi: 10.1177/1078155214538087. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2015. PMID: 24917416 Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 and immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer.Cancer Lett. 2017 Oct 28;407:57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28826722 Review.
-
Control of peripheral T-cell tolerance and autoimmunity via the CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways.Immunol Rev. 2008 Aug;224:166-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00662.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18759926 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular adverse events and immune-related adverse events associated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 29;14(1):25919. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75099-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39472591 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated gene signature to predict the immune status and prognosis of cutaneous melanoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 9;101(36):e30280. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030280. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36086718 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of programmed cell death 1 by interferon gamma and its biological functions in human monocytes.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Oct 17;32:101369. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101369. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36275930 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of first-line treatments for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Thorac Cancer. 2019 Apr;10(4):607-623. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12971. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30734504 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage repair-related gene signature for identifying the immune status and predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 3;13(1):18978. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45999-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37923899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Latchman Y, et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:261–268. - PubMed
-
- Yamazaki T, et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine T cells and APC. J. Immunol. 2002;169:5538–5545. - PubMed
-
- Agata Y, et al. Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int. Immunol. 1996;8:765–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

