Transcriptomic-Wide Discovery of Direct and Indirect HuR RNA Targets in Activated CD4+ T Cells
- PMID: 26162078
- PMCID: PMC4498740
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129321
Transcriptomic-Wide Discovery of Direct and Indirect HuR RNA Targets in Activated CD4+ T Cells
Abstract
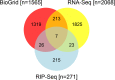
Due to poor correlation between steady state mRNA levels and protein product, purely transcriptomic profiling methods may miss genes posttranscriptionally regulated by RNA binding proteins (RBPs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) methods developed to identify in vivo targets of RBPs have greatly elucidated those mRNAs which may be regulated via transcript stability and translation. The RBP HuR (ELAVL1) and family members are major stabilizers of mRNA. Many labs have identified HuR mRNA targets; however, many of these analyses have been performed in cell lines and oftentimes are not independent biological replicates. Little is known about how HuR target mRNAs behave in conditional knock-out models. In the present work, we performed HuR RIP-Seq and RNA-Seq to investigate HuR direct and indirect targets using a novel conditional knock-out model of HuR genetic ablation during CD4+ T activation and Th2 differentiation. Using independent biological replicates, we generated a high coverage RIP-Seq data set (>160 million reads) that was analyzed using bioinformatics methods specifically designed to find direct mRNA targets in RIP-Seq data. Simultaneously, another set of independent biological replicates were sequenced by RNA-Seq (>425 million reads) to identify indirect HuR targets. These direct and indirect targets were combined to determine canonical pathways in CD4+ T cell activation and differentiation for which HuR plays an important role. We show that HuR may regulate genes in multiple canonical pathways involved in T cell activation especially the CD28 family signaling pathway. These data provide insights into potential HuR-regulated genes during T cell activation and immune mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of tumorigenesis-related mRNAs associated with RNA-binding protein HuR in thyroid cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 27;7(39):63388-63407. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11255. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27542231 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional knockout of the RNA-binding protein HuR in CD4⁺ T cells reveals a gene dosage effect on cytokine production.Mol Med. 2014 Mar 20;20(1):93-108. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2013.00127. Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24477678 Free PMC article.
-
DO-RIP-seq to quantify RNA binding sites transcriptome-wide.Methods. 2017 Apr 15;118-119:16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.11.004. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Methods. 2017. PMID: 27840290 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of the regulatory RNA-binding protein HuR and its role in controlling miRNA repression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;700:106-23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 21627034 Review.
-
Dysregulation of TTP and HuR plays an important role in cancers.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):14451-14461. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5397-z. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27644249 Review.
Cited by
-
HIV vaccine candidate efficacy in female macaques mediated by cAMP-dependent efferocytosis and V2-specific ADCC.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 2;14(1):575. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36109-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36732510 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of RNA-binding protein HuR and miR-466i regulates GM-CSF expression.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 8;7(1):17233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17371-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29222492 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle RNA regulons coordinating early lymphocyte development.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017 Sep;8(5):e1419. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1419. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. PMID: 28231639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of tumorigenesis-related mRNAs associated with RNA-binding protein HuR in thyroid cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 27;7(39):63388-63407. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11255. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27542231 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Profile of Six RNA-Binding Proteins in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 30;11(8):e0161669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161669. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27575817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calaluce R, Gubin MM, Davis JW, Magee JD, Chen J, Kuwano Y, et al. The RNA binding protein HuR differentially regulates unique subsets of mRNAs in estrogen receptor negative and estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:126. Epub 2010/04/08. doi: 1471-2407-10-126 [pii]10.1186/1471-2407-10-126 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atasoy U, Watson J, Patel D, Keene JD. ELAV protein HuA (HuR) can redistribute between nucleus and cytoplasm and is upregulated during serum stimulation and T cell activation. J Cell Sci. 1998;111 (Pt 21):3145–56. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

