Thermodynamics of long supercoiled molecules: insights from highly efficient Monte Carlo simulations
- PMID: 26153710
- PMCID: PMC4571024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.005
Thermodynamics of long supercoiled molecules: insights from highly efficient Monte Carlo simulations
Abstract
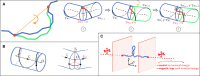
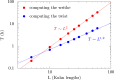
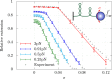
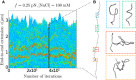
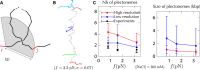
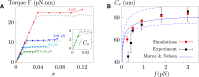
Supercoiled DNA polymer models for which the torsional energy depends on the total twist of molecules (Tw) are a priori well suited for thermodynamic analysis of long molecules. So far, nevertheless, the exact determination of Tw in these models has been based on a computation of the writhe of the molecules (Wr) by exploiting the conservation of the linking number, Lk=Tw+Wr, which reflects topological constraints coming from the helical nature of DNA. Because Wr is equal to the number of times the main axis of a DNA molecule winds around itself, current Monte Carlo algorithms have a quadratic time complexity, O(L(2)), with respect to the contour length (L) of the molecules. Here, we present an efficient method to compute Tw exactly, leading in principle to algorithms with a linear complexity, which in practice is O(L(1.2)). Specifically, we use a discrete wormlike chain that includes the explicit double-helix structure of DNA and where the linking number is conserved by continuously preventing the generation of twist between any two consecutive cylinders of the discretized chain. As an application, we show that long (up to 21 kbp) linear molecules stretched by mechanical forces akin to magnetic tweezers contain, in the buckling regime, multiple and branched plectonemes that often coexist with curls and helices, and whose length and number are in good agreement with experiments. By attaching the ends of the molecules to a reservoir of twists with which these can exchange helix turns, we also show how to compute the torques in these models. As an example, we report values that are in good agreement with experiments and that concern the longest molecules that have been studied so far (16 kbp).
Copyright © 2015 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conformational and thermodynamic properties of supercoiled DNA.J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1224-43. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90533-p. J Mol Biol. 1992. PMID: 1433295
-
Conformational and thermodynamic properties of supercoiled DNA.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:609-43. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.003141. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994. PMID: 7919794 Review.
-
Computer simulation of DNA supercoiling.J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):413-9. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90745-r. J Mol Biol. 1991. PMID: 1994032
-
Evaluating changes of writhe in computer simulations of supercoiled DNA.J Chem Phys. 2005 Feb 8;122(6):064905. doi: 10.1063/1.1846052. J Chem Phys. 2005. PMID: 15740406
-
DNA twist as a transcriptional sensor for environmental changes.Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1861-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01358.x. Mol Microbiol. 1992. PMID: 1508037 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA supercoiling in bacteria: state of play and challenges from a viewpoint of physics based modeling.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 30;14:1192831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1192831. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37965550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA elasticity from coarse-grained simulations: The effect of groove asymmetry.J Chem Phys. 2017 Jun 7;146(21):214902. doi: 10.1063/1.4984039. J Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 28595422 Free PMC article.
-
Coarse-grained modelling of DNA plectoneme pinning in the presence of base-pair mismatches.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Nov 4;48(19):10713-10725. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa836. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 33045724 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the salt dependence of the torsional stiffness of DNA by multiplexed magnetic torque tweezers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2;45(10):5920-5929. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx280. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28460037 Free PMC article.
-
Supercoiled DNA and non-equilibrium formation of protein complexes: A quantitative model of the nucleoprotein ParBS partition complex.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Apr 16;17(4):e1008869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008869. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33861734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vologodskii A.V., Cozzarelli N.R. Conformational and thermodynamic properties of supercoiled DNA. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1994;23:609–643. - PubMed
-
- Strick T.R., Dessinges M.-N., Croquette V. Stretching of macromolecules and proteins. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2003;66:1–46.
-
- Travers A., Muskhelishvili G. DNA supercoiling—a global transcriptional regulator for enterobacterial growth? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005;3:157–169. - PubMed
-
- Benza V.G., Bassetti B., Lagomarsino M.C. Physical descriptions of the bacterial nucleoid at large scales, and their biological implications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012;75:076602. - PubMed
-
- Junier I. Conserved patterns in bacterial genomes: a conundrum physically tailored by evolutionary tinkering. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2014;53 Pt A:125–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

