Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 in Physiological and Pathophysiological Angiogenesis: Applications and Therapies
- PMID: 26146622
- PMCID: PMC4471260
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/549412
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 in Physiological and Pathophysiological Angiogenesis: Applications and Therapies
Abstract
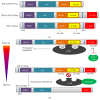
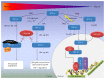
The cardiovascular system ensures the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, tissues, and organs. Under extended exposure to reduced oxygen levels, cells are able to survive through the transcriptional activation of a series of genes that participate in angiogenesis, glucose metabolism, and cell proliferation. The oxygen-sensitive transcriptional activator HIF-1 (hypoxia-inducible factor-1) is a key transcriptional mediator of the response to hypoxic conditions. The HIF-1 pathway was found to be a master regulator of angiogenesis. Whether the process is physiological or pathological, HIF-1 seems to participate in vasculature formation by synergistic correlations with other proangiogenic factors such as VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), PlGF (placental growth factor), or angiopoietins. Considering the important contributions of HIF-1 in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis, it should be considered a promising target for treating ischaemic diseases or cancer. In this review, we discuss the roles of HIF-1 in both physiological/pathophysiological angiogenesis and potential strategies for clinical therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha in angiogenesis.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Dec;233(12):9087-9098. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26805. Epub 2018 Jul 3. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29968905 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediates activation of cultured vascular endothelial cells by inducing multiple angiogenic factors.Circ Res. 2003 Oct 3;93(7):664-73. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000093984.48643.D7. Epub 2003 Sep 4. Circ Res. 2003. PMID: 12958144
-
Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1.Circ Res. 2003 Nov 28;93(11):1074-81. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000102937.50486.1B. Epub 2003 Oct 23. Circ Res. 2003. PMID: 14576200
-
The redox protein thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) increases hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein expression: Trx-1 overexpression results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor production and enhanced tumor angiogenesis.Cancer Res. 2002 Sep 1;62(17):5089-95. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12208766
-
Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2006;76:217-57. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(06)76007-0. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 17118268 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Pericytes in Inner Ear Disorders: A Comprehensive Review.Biology (Basel). 2024 Oct 8;13(10):802. doi: 10.3390/biology13100802. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin Downregulates Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression and HIF-1α/VEGF Signaling-Related Angiogenesis in a Mouse Model of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Aug 22;2020:9485398. doi: 10.1155/2020/9485398. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32908926 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha expression in osteosarcoma: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Mar 14;9:1477-87. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S95490. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27042116 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Physiological and Pathological Angiogenesis in Retinopathy of Prematurity and Emerging Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 1;22(9):4809. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094809. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34062733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal High Linoleic Acid Alters Placental Fatty Acid Composition.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 23;12(8):2183. doi: 10.3390/nu12082183. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32717842 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

