Identification of in vivo DNA-binding mechanisms of Pax6 and reconstruction of Pax6-dependent gene regulatory networks during forebrain and lens development
- PMID: 26138486
- PMCID: PMC4538810
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv589
Identification of in vivo DNA-binding mechanisms of Pax6 and reconstruction of Pax6-dependent gene regulatory networks during forebrain and lens development
Abstract
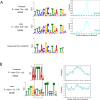
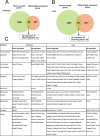
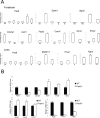
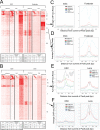
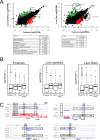
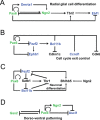
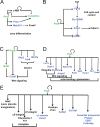
The transcription factor Pax6 is comprised of the paired domain (PD) and homeodomain (HD). In the developing forebrain, Pax6 is expressed in ventricular zone precursor cells and in specific subpopulations of neurons; absence of Pax6 results in disrupted cell proliferation and cell fate specification. Pax6 also regulates the entire lens developmental program. To reconstruct Pax6-dependent gene regulatory networks (GRNs), ChIP-seq studies were performed using forebrain and lens chromatin from mice. A total of 3514 (forebrain) and 3723 (lens) Pax6-containing peaks were identified, with ∼70% of them found in both tissues and thereafter called 'common' peaks. Analysis of Pax6-bound peaks identified motifs that closely resemble Pax6-PD, Pax6-PD/HD and Pax6-HD established binding sequences. Mapping of H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, H3K27me3 and RNA polymerase II revealed distinct types of tissue-specific enhancers bound by Pax6. Pax6 directly regulates cortical neurogenesis through activation (e.g. Dmrta1 and Ngn2) and repression (e.g. Ascl1, Fezf2, and Gsx2) of transcription factors. In lens, Pax6 directly regulates cell cycle exit via components of FGF (Fgfr2, Prox1 and Ccnd1) and Wnt (Dkk3, Wnt7a, Lrp6, Bcl9l, and Ccnd1) signaling pathways. Collectively, these studies provide genome-wide analysis of Pax6-dependent GRNs in lens and forebrain and establish novel roles of Pax6 in organogenesis.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pax6 interactions with chromatin and identification of its novel direct target genes in lens and forebrain.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054507. Epub 2013 Jan 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23342162 Free PMC article.
-
The orchestration of mammalian tissue morphogenesis through a series of coherent feed-forward loops.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):43259-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.264580. Epub 2011 Oct 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21998302 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of pax6-dependent gene regulatory networks in the mouse lens.PLoS One. 2009;4(1):e4159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004159. Epub 2009 Jan 9. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19132093 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of gene expression by Pax6 in ocular cells: a case of tissue-preferred expression of crystallins in lens.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(8-9):829-44. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041866ac. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15558475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of Pax6 and SOX2 in lens development as a paradigm of genetic switch mechanisms for cell differentiation.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(8-9):819-27. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041868hk. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15558474 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-binding proteins in eye development and disease: implication of conserved RNA granule components.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Jul;7(4):527-57. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1355. Epub 2016 May 1. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27133484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pax6 associates with H3K4-specific histone methyltransferases Mll1, Mll2, and Set1a and regulates H3K4 methylation at promoters and enhancers.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016 Sep 9;9(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13072-016-0087-z. eCollection 2016. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016. PMID: 27617035 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic Variation in a Four-Generation Family with Aniridia Carrying a Novel PAX6 Mutation.J Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr 4;2018:5978293. doi: 10.1155/2018/5978293. eCollection 2018. J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29850208 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage specific transcription factors and epigenetic regulators mediate TGFβ-dependent enhancer activation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Apr 20;46(7):3351-3365. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky093. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29438503 Free PMC article.
-
The developmental hourglass model is applicable to the spinal cord based on single-cell transcriptomes and non-conserved cis-regulatory elements.Dev Growth Differ. 2021 Sep;63(7):372-391. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12750. Dev Growth Differ. 2021. PMID: 34473348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Georgala P.A., Carr C.B., Price D.J. The role of Pax6 in forebrain development. Dev. Neurobiol. 2011;71:690–709. - PubMed
-
- Nikoletopoulou V., Plachta N., Allen N.D., Pinto L., Gotz M., Barde Y.A. Neurotrophin receptor-mediated death of misspecified neurons generated from embryonic stem cells lacking Pax6. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:529–540. - PubMed
-
- Weinandy F., Ninkovic J., Gotz M. Restrictions in time and space–new insights into generation of specific neuronal subtypes in the adult mammalian brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011;33:1045–1054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

