Salmon Gill Poxvirus, the Deepest Representative of the Chordopoxvirinae
- PMID: 26136578
- PMCID: PMC4542343
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01174-15
Salmon Gill Poxvirus, the Deepest Representative of the Chordopoxvirinae
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Gjessing et al., Salmon Gill Poxvirus, the Deepest Representative of the Chordopoxvirinae.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(21):11174. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02125-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26432522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
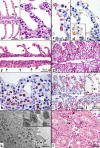
Poxviruses are large DNA viruses of vertebrates and insects causing disease in many animal species, including reptiles, birds, and mammals. Although poxvirus-like particles were detected in diseased farmed koi carp, ayu, and Atlantic salmon, their genetic relationships to poxviruses were not established. Here, we provide the first genome sequence of a fish poxvirus, which was isolated from farmed Atlantic salmon. In the present study, we used quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry to determine aspects of salmon gill poxvirus disease, which are described here. The gill was the main target organ where immature and mature poxvirus particles were detected. The particles were detected in detaching, apoptotic respiratory epithelial cells preceding clinical disease in the form of lethargy, respiratory distress, and mortality. In moribund salmon, blocking of gas exchange would likely be caused by the adherence of respiratory lamellae and epithelial proliferation obstructing respiratory surfaces. The virus was not found in healthy salmon or in control fish with gill disease without apoptotic cells, although transmission remains to be demonstrated. PCR of archival tissue confirmed virus infection in 14 cases with gill apoptosis in Norway starting from 1995. Phylogenomic analyses showed that the fish poxvirus is the deepest available branch of chordopoxviruses. The virus genome encompasses most key chordopoxvirus genes that are required for genome replication and expression, although the gene order is substantially different from that in other chordopoxviruses. Nevertheless, many highly conserved chordopoxvirus genes involved in viral membrane biogenesis or virus-host interactions are missing. Instead, the salmon poxvirus carries numerous genes encoding unknown proteins, many of which have low sequence complexity and contain simple repeats suggestive of intrinsic disorder or distinct protein structures.
Importance: Aquaculture is an increasingly important global source of high-quality food. To sustain the growth in aquaculture, disease control in fish farming is essential. Moreover, the spread of disease from farmed fish to wildlife is a concern. Serious poxviral diseases are emerging in aquaculture, but very little is known about the viruses and the diseases that they cause. There is a possibility that viruses with enhanced virulence may spread to new species, as has occurred with the myxoma poxvirus in rabbits. Provision of the first fish poxvirus genome sequence and specific diagnostics for the salmon gill poxvirus in Atlantic salmon may help curb this disease and provide comparative knowledge. Furthermore, because salmon gill poxvirus represents the deepest branch of chordopoxvirus so far discovered, the genome analysis provided substantial insight into the evolution of different functional modules in this important group of viruses.
Copyright © 2015, Gjessing et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Morphogenesis of salmonid gill poxvirus associated with proliferative gill disease in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in Norway.Arch Virol. 2008;153(7):1299-309. doi: 10.1007/s00705-008-0117-7. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Arch Virol. 2008. PMID: 18521535
-
The Atlantic Salmon Gill Transcriptome Response in a Natural Outbreak of Salmon Gill Pox Virus Infection Reveals New Biomarkers of Gill Pathology and Suppression of Mucosal Defense.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 4;11:2154. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02154. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013908 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal and Systemic Immune Responses to Salmon Gill Poxvirus Infection in Atlantic Salmon Are Modulated Upon Hydrocortisone Injection.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 9;12:689302. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.689302. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34177946 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of Salmon Gill Poxvirus.Viruses. 2022 Dec 1;14(12):2701. doi: 10.3390/v14122701. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36560705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmon gill poxvirus, a recently characterized infectious agent of multifactorial gill disease in freshwater- and seawater-reared Atlantic salmon.J Fish Dis. 2017 Oct;40(10):1253-1265. doi: 10.1111/jfd.12608. Epub 2017 Jan 20. J Fish Dis. 2017. PMID: 28105681 Review.
Cited by
-
Genotyping of Salmon Gill Poxvirus Reveals One Main Predominant Lineage in Europe, Featuring Fjord- and Fish Farm-Specific Sub-Lineages.Front Microbiol. 2020 May 29;11:1071. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01071. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32547516 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-agent in situ hybridization confirms Ca. Branchiomonas cysticola as a major contributor in complex gill disease in Atlantic salmon.Fish Shellfish Immunol Rep. 2021 Sep 6;2:100026. doi: 10.1016/j.fsirep.2021.100026. eCollection 2021 Dec. Fish Shellfish Immunol Rep. 2021. PMID: 36420507 Free PMC article.
-
The 2.1 Å structure of protein F9 and its comparison to L1, two components of the conserved poxvirus entry-fusion complex.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 14;8(1):16807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34244-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30429486 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Marine Gill Disease in Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) in Chile Using a Novel Total Gross Gill Scoring System: A Case Study.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 16;9(12):2605. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122605. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34946205 Free PMC article.
-
Genotyping tool for salmonid gill pox virus (SGPV) obtained from farmed and wild Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar).Arch Virol. 2023 Sep 8;168(10):249. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05866-8. Arch Virol. 2023. PMID: 37684418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ono S, Nagai A, Sugai N. 1986. A histopathological study on juvenile colorcarp, Cyprinus carpio, showing edema. Fish Pathol 9:9.
-
- Wada S, Kurata O, Hatai K, Ishii H, Kasuya K, Watanabe Y. 2008. Proliferative branchitis associated with pathognomonic, atypical gill epithelial cells in cultured ayu Plecoglossus altivelis. Fish Pathol 43:89–91. doi:10.3147/jsfp.43.89. - DOI
-
- Oyamatsu T, Matoyama H, Yamamoto K-Y, Fukuda H. 1997. A trial for the detection of carp edema virus by using polymerase chain reaction. Aquaculture Sci 45:247–251.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

