γδ T Cells Are Required for M2 Macrophage Polarization and Resolution of Ozone-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation in Mice
- PMID: 26135595
- PMCID: PMC4489797
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131236
γδ T Cells Are Required for M2 Macrophage Polarization and Resolution of Ozone-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation in Mice
Abstract
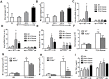
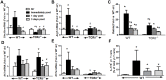
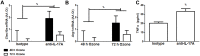
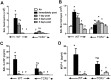
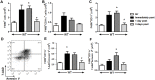
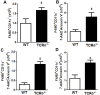
We examined the role of γδ T cells in the induction of alternatively activated M2 macrophages and the resolution of inflammation after ozone exposure. Wildtype (WT) mice and mice deficient in γδ T cells (TCRδ-/- mice) were exposed to air or to ozone (0.3 ppm for up to 72h) and euthanized immediately or 1, 3, or 5 days after cessation of exposure. In WT mice, M2 macrophages accumulated in the lungs over the course of ozone exposure. Pulmonary mRNA abundance of the M2 genes, Arg1, Retnla, and Clec10a, also increased after ozone. In contrast, no evidence of M2 polarization was observed in TCRδ-/- mice. WT but not TCRδ-/- mice expressed the M2c polarizing cytokine, IL-17A, after ozone exposure and WT mice treated with an IL-17A neutralizing antibody exhibited attenuated ozone-induced M2 gene expression. In WT mice, ozone-induced increases in bronchoalveolar lavage neutrophils and macrophages resolved quickly after cessation of ozone exposure returning to air exposed levels within 3 days. However, lack of M2 macrophages in TCRδ-/- mice was associated with delayed clearance of inflammatory cells after cessation of ozone and increased accumulation of apoptotic macrophages in the lungs. Delayed restoration of normal lung architecture was also observed in TCRδ-/- mice. In summary, our data indicate that γδ T cells are required for the resolution of ozone-induced inflammation, likely because γδ T cells, through their secretion of IL-17A, contribute to changes in macrophage polarization that promote clearance of apoptotic cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
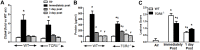
Similar articles
-
γδ T cells are required for pulmonary IL-17A expression after ozone exposure in mice: role of TNFα.PLoS One. 2014 May 13;9(5):e97707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097707. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24823369 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary inflammation induced by subacute ozone is augmented in adiponectin-deficient mice: role of IL-17A.J Immunol. 2012 May 1;188(9):4558-67. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102363. Epub 2012 Apr 2. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22474022 Free PMC article.
-
Innate cellular sources of interleukin-17A regulate macrophage accumulation in cigarette- smoke-induced lung inflammation in mice.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Nov;129(9):785-96. doi: 10.1042/CS20140703. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26201093 Free PMC article.
-
The mutual regulation between γδ T cells and macrophages during wound healing.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Apr 29;115(5):840-851. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiad087. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 37493223 Review.
-
Lung-resident γδ T cells and their roles in lung diseases.Immunology. 2017 Aug;151(4):375-384. doi: 10.1111/imm.12764. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28555812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Compartment-specific transcriptomics of ozone-exposed murine lungs reveals sex- and cell type-associated perturbations relevant to mucoinflammatory lung diseases.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021 Jan 1;320(1):L99-L125. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00381.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33026818 Free PMC article.
-
Ozone-Induced Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation Controls Lung Inflammation via Interleukin-22 Modulation.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 25;11:144. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00144. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32161582 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular and extravesicular protein analyses from the airspaces of ozone-exposed mice revealed signatures associated with mucoinflammatory lung disease.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 1;11(1):23203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02256-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34853335 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of mTORC1 Activity in CD4+ T Cells Is Associated with Lung Fibrosis and Increased γδ T Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 20;11(9):e0163288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163288. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27649073 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Transcriptomes Reveal a Complex Cellular Landscape in the Middle Ear and Differential Capacities for Acute Response to Infection.Front Genet. 2020 Apr 15;11:358. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00358. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32351546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devlin RB, McDonnell WF, Mann R, Becker S, House DE, Schreinemachers D, et al. (1991) Exposure of Humans to Ambient Levels of Ozone for 6.6 Hours Causes Cellular and Biochemical Changes in the Lung. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 4: 72–81. - PubMed
-
- Levy JI, Chemerynski SM, Sarnat JA (2005) Ozone Exposure and Mortality: An Empiric Bayes Metaregression Analysis. Epidemiology 16: 458–468 410.1097/1001.ede.0000165820.0000108301.b0000165823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

