Structure of a Bud6/Actin Complex Reveals a Novel WH2-like Actin Monomer Recruitment Motif
- PMID: 26118535
- PMCID: PMC4578302
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2015.05.015
Structure of a Bud6/Actin Complex Reveals a Novel WH2-like Actin Monomer Recruitment Motif
Abstract
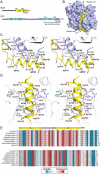
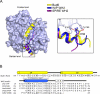
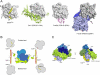
In budding yeast, the actin-binding protein Bud6 cooperates with formins Bni1 and Bnr1 to catalyze the assembly of actin filaments. The nucleation-enhancing activity of Bud6 requires both a "core" domain that binds to the formin and a "flank" domain that binds monomeric actin. Here, we describe the structure of the Bud6 flank domain in complex with actin. Two helices in Bud6(flank) interact with actin; one binds in a groove at the barbed end of the actin monomer in a manner closely resembling the helix of WH2 domains, a motif found in many actin nucleation factors. The second helix rises along the face of actin. Mutational analysis verifies the importance of these Bud6-actin contacts for nucleation-enhancing activity. The Bud6 binding site on actin overlaps with that of the formin FH2 domain and is also incompatible with inter-subunit contacts in F-actin, suggesting that Bud6 interacts only transiently with actin monomers during filament nucleation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
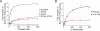
Similar articles
-
Structure of the formin-interaction domain of the actin nucleation-promoting factor Bud6.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 11;109(50):E3424-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203035109. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23161908 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activities and regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae formin proteins Bni1 and Bnr1 by Bud6.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 29;280(30):28023-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503094200. Epub 2005 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15923184
-
Mechanism and cellular function of Bud6 as an actin nucleation-promoting factor.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Nov;22(21):4016-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-05-0404. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21880892 Free PMC article.
-
The WH2 Domain and Actin Nucleation: Necessary but Insufficient.Trends Biochem Sci. 2016 Jun;41(6):478-490. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016. PMID: 27068179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WH2 domain: a small, versatile adapter for actin monomers.FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):92-7. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03242-2. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11911886 Review.
Cited by
-
Yeast as a Model to Understand Actin-Mediated Cellular Functions in Mammals-Illustrated with Four Actin Cytoskeleton Proteins.Cells. 2020 Mar 10;9(3):672. doi: 10.3390/cells9030672. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32164332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated control of formin-mediated actin assembly by a stationary inhibitor and a mobile activator.J Cell Biol. 2018 Oct 1;217(10):3512-3530. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201803164. Epub 2018 Aug 3. J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30076201 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the C-terminal Extension of Formin 2 in Its Activation by Spire Protein and Processive Assembly of Actin Filaments.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 12;291(7):3302-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.681379. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26668326 Free PMC article.
-
Non-catalytic signaling by pseudokinase ILK for regulating cell adhesion.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 26;9(1):4465. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06906-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30367047 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of yeast formins and their regulators Bud6 and Bil2 in the pheromone response.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Jun 1;35(6):ar85. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-11-0459. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38656798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosch M, Le KH, Bugyi B, Correia JJ, Renault L, Carlier MF. Analysis of the function of Spire in actin assembly and its synergy with formin and profilin. Mol Cell. 2007;28:555–568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

