Core oxidative stress response in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 26115917
- PMCID: PMC4482186
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-1705-z
Core oxidative stress response in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
Background: The b-Zip transcription factor AtfA plays a key role in regulating stress responses in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. To identify the core regulons of AtfA, we examined genome-wide expression changes caused by various stresses in the presence/absence of AtfA using A. nidulans microarrays. We also intended to address the intriguing question regarding the existence of core environmental stress response in this important model eukaryote.
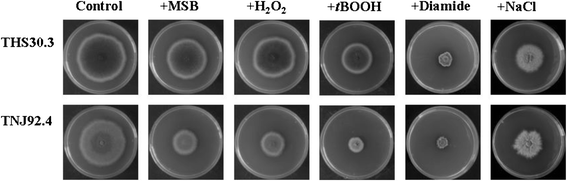
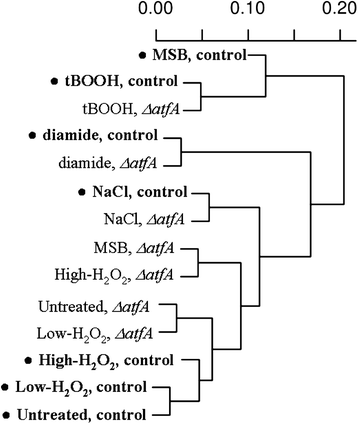
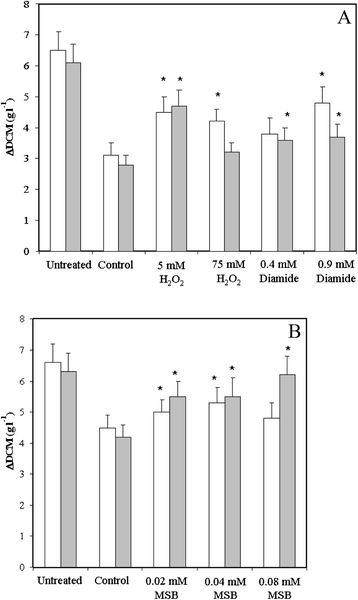
Results: Examination of the genome wide expression changes caused by five different oxidative stress conditions in wild type and the atfA null mutant has identified a significant number of stereotypically regulated genes (Core Oxidative Stress Response genes). The deletion of atfA increased the oxidative stress sensitivity of A. nidulans and affected mRNA accumulation of several genes under both unstressed and stressed conditions. The numbers of genes under the AtfA control appear to be specific to a stress-type. We also found that both oxidative and salt stresses induced expression of some secondary metabolite gene clusters and the deletion of atfA enhanced the stress responsiveness of additional clusters. Moreover, certain clusters were down-regulated by the stresses tested.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that the observed co-regulations were most likely consequences of the overlapping physiological effects of the stressors and not of the existence of a general environmental stress response. The function of AtfA in governing various stress responses is much smaller than anticipated and/or other regulators may play a redundant or overlapping role with AtfA. Both stress inducible and stress repressive regulations of secondary metabolism seem to be frequent features in A. nidulans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AtfA bZIP-type transcription factor regulates oxidative and osmotic stress responses in Aspergillus nidulans.Mol Genet Genomics. 2010 Mar;283(3):289-303. doi: 10.1007/s00438-010-0513-z. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Mol Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20131067
-
Genome-Wide Gene Expression Analyses of the AtfA/AtfB-Mediated Menadione Stress Response in Aspergillus nidulans.Cells. 2023 Jan 31;12(3):463. doi: 10.3390/cells12030463. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766807 Free PMC article.
-
General stress response or adaptation to rapid growth in Aspergillus nidulans?Fungal Biol. 2020 May;124(5):376-386. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2019.10.009. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Fungal Biol. 2020. PMID: 32389300
-
Expression of asexual developmental regulator gene abaA is affected in the double mutants of classes I and II chitin synthase genes, chsC and chsA, of Aspergillus nidulans.Curr Genet. 2005 Sep;48(3):171-83. doi: 10.1007/s00294-005-0004-7. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Curr Genet. 2005. PMID: 16082523 Review.
-
The impact of bZIP Atf1ortholog global regulators in fungi.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Aug;105(14-15):5769-5783. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11431-7. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34302199 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global Transcriptomic Changes Elicited by sodB Deletion and Menadione Exposure in Aspergillus nidulans.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Oct 30;9(11):1060. doi: 10.3390/jof9111060. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998866 Free PMC article.
-
Two New Aspergillus flavus Reference Genomes Reveal a Large Insertion Potentially Contributing to Isolate Stress Tolerance and Aflatoxin Production.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Oct 5;10(10):3515-3531. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401405. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32817124 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress Response of Aspergillus oryzae Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide and Menadione Sodium Bisulfite.Microorganisms. 2019 Jul 30;7(8):225. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7080225. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31366149 Free PMC article.
-
Collection and Curation of Transcriptional Regulatory Interactions in Aspergillus nidulans and Neurospora crassa Reveal Structural and Evolutionary Features of the Regulatory Networks.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jan 19;9:27. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00027. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29403467 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Components of Pomegranate Oil and Their Influence on Mycotoxin Secretion.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 27;12(12):748. doi: 10.3390/toxins12120748. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33260849 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

