Identification of small molecule inhibitors of Zcchc11 TUTase activity
- PMID: 26114892
- PMCID: PMC4615740
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1058478
Identification of small molecule inhibitors of Zcchc11 TUTase activity
Abstract
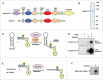
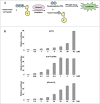
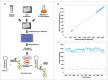
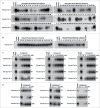
The RNA-binding protein Lin28 regulates the expression of the let-7 family of microRNAs (miRNAs) during early embryonic development. Lin28 recruits the 3' terminal uridylyl transferase (TUTase) Zcchc11 (TUT4) and/or Zcchc6 (TUT7) to precursor let-7 RNA (pre-let-7) to selectively block let-7 biogenesis. Uridylated pre-let-7 is targeted for decay by the downstream exonuclease Dis3l2 thereby preventing processing to mature let-7. Activation of this oncogenic pathway via up-regulation of Lin28 expression promotes cellular transformation, drives tumorigenesis in mouse models, and is frequently observed in a wide variety of cancer. Recent proof-of-principle experiments showed that Zcchc11 knockdown inhibits the tumorigenicity of Lin28-expressing human cancer cells and established this enzyme as a possible new therapeutic target for human malignancies. However, there are currently no known pharmacological agents capable of targeting this novel enzyme. In this study we developed and applied a sensitive biochemical assay that monitors Zcchc11 activity. Using this assay we performed an automated high-throughput screen of ∼ 15,000 chemicals to identify putative TUTase inhibitors. Several of these small molecules were validated as specific inhibitors of Zcchc11 activity. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of screening for TUTase inhibitors and present a relatively simple platform that can be exploited for future drug discovery efforts aimed at restoring let-7 expression in cancer.
Keywords: Lin28; TUT4; TUTase; Zcchc11; cancer; let-7; miRNA; microRNA; uridylation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The LIN28/let-7 Pathway in Cancer.Front Genet. 2017 Mar 28;8:31. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00031. eCollection 2017. Front Genet. 2017. PMID: 28400788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3' RNA Uridylation in Epitranscriptomics, Gene Regulation, and Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jul 13;5:61. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00061. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30057901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lin28-mediated control of let-7 microRNA expression by alternative TUTases Zcchc11 (TUT4) and Zcchc6 (TUT7).RNA. 2012 Oct;18(10):1875-85. doi: 10.1261/rna.034538.112. Epub 2012 Aug 16. RNA. 2012. PMID: 22898984 Free PMC article.
-
Lin28 recruits the TUTase Zcchc11 to inhibit let-7 maturation in mouse embryonic stem cells.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Oct;16(10):1021-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1676. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19713958 Free PMC article.
-
Selective microRNA uridylation by Zcchc6 (TUT7) and Zcchc11 (TUT4).Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Oct;42(18):11777-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku805. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25223788 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The LIN28/let-7 Pathway in Cancer.Front Genet. 2017 Mar 28;8:31. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00031. eCollection 2017. Front Genet. 2017. PMID: 28400788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL1 promotes neuroblastoma development through m7G tRNA modification and selective oncogenic gene translation.Biomark Res. 2022 Sep 7;10(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00414-z. Biomark Res. 2022. PMID: 36071474 Free PMC article.
-
Dis3l2-Mediated Decay Is a Quality Control Pathway for Noncoding RNAs.Cell Rep. 2016 Aug 16;16(7):1861-73. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.025. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27498873 Free PMC article.
-
3' RNA Uridylation in Epitranscriptomics, Gene Regulation, and Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jul 13;5:61. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00061. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30057901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying and characterizing functional 3' nucleotide addition in the miRNA pathway.Methods. 2019 Jan 1;152:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.08.006. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Methods. 2019. PMID: 30138674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Croce CM. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10:704-14; PMID:19763153; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrg2634 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davalos V, Esteller M. MicroRNAs and cancer epigenetics: a macrorevolution. Curr Opin Oncol 2010; 22:35-45; PMID:19907325; http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCO.0b013e328333dcbb - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lin S, Gregory RI. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2015; 15:321-33; PMID:25998712; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc3932 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peter ME. Let-7 and miR-200 microRNAs: guardians against pluripotency and cancer progression. Cell Cycle 2009; 8:843-52; PMID:19221491; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/cc.8.6.7907 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
