Clarithromycin Attenuates Radiation-Induced Lung Injury in Mice
- PMID: 26114656
- PMCID: PMC4482753
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131671
Clarithromycin Attenuates Radiation-Induced Lung Injury in Mice
Abstract
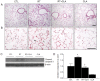
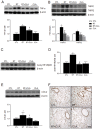
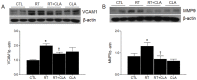
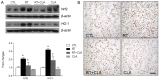
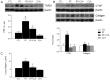
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a common and unavoidable complication of thoracic radiotherapy. The current study was conducted to evaluate the ability of clarithromycin (CLA) to prevent radiation-induced pneumonitis, oxidative stress, and lung fibrosis in an animal model. C57BL/6J mice were assigned to control, irradiation only, irradiation plus CLA, and CLA only groups. Test mice received single thoracic exposures to radiation and/or oral CLA (100 mg/kg/day). Histopathologic findings and markers of inflammation, fibrosis, and oxidative stress were compared by group. On a microscopic level, CLA inhibited macrophage influx, alveolar fibrosis, parenchymal collapse, consolidation, and epithelial cell changes. The concentration of collagen in lung tissue was lower in irradiation plus CLA mice. Radiation-induced expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, TNF receptor 1, acetylated nuclear factor kappa B, cyclooxygenase 2, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, and matrix metallopeptidase 9 were also attenuated by CLA. Expression levels of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and heme oxygenase 1, transforming growth factor-β1, connective tissue growth factor, and type I collagen in radiation-treated lungs were also attenuated by CLA. These findings indicate that CLA ameliorates the deleterious effects of thoracic irradiation in mice by reducing pulmonary inflammation, oxidative damage, and fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic polyethylene glycol-modified (PEGylated) superoxide dismutase and catalase mixture attenuates radiation pulmonary fibrosis in the C57/bl6 mouse.Radiother Oncol. 2006 Nov;81(2):196-205. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2006.09.013. Epub 2006 Oct 27. Radiother Oncol. 2006. PMID: 17069914 Free PMC article.
-
Polydatin alleviated radiation-induced lung injury through activation of Sirt3 and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Dec;21(12):3264-3276. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13230. Epub 2017 Jun 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28609013 Free PMC article.
-
Subcutaneous administration of bovine superoxide dismutase protects lungs from radiation-induced lung injury.Free Radic Res. 2015 Oct;49(10):1259-1268. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2015.1066501. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Free Radic Res. 2015. PMID: 26110460 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation and the lung: a reevaluation of the mechanisms mediating pulmonary injury.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995 Jan 15;31(2):361-9. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)00477-3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995. PMID: 7836090 Review.
-
Modeling radiation-induced lung injury: lessons learned from whole thorax irradiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2020 Jan;96(1):129-144. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2018.1532619. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Int J Radiat Biol. 2020. PMID: 30359147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clarithromycin synergizes with cisplatin to inhibit ovarian cancer growth in vitro and in vivo.J Ovarian Res. 2019 Nov 8;12(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13048-019-0570-9. J Ovarian Res. 2019. PMID: 31703731 Free PMC article.
-
Early variations in lymphocytes and T lymphocyte subsets are associated with radiation pneumonitis in lung cancer patients and experimental mice received thoracic irradiation.Cancer Med. 2020 May;9(10):3437-3444. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2987. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32207253 Free PMC article.
-
Clarithromycin mitigates radiation pneumonitis in patients with lung cancer treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Jan;10(1):247-261. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.12.22. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 29600055 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Inflammation and Radiation-Induced Cystitis: Molecular Background and Therapeutic Perspectives.Cells. 2020 Dec 24;10(1):21. doi: 10.3390/cells10010021. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33374374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Combination of Podophyllotoxin and Rutin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pneumonitis and Fibrosis through Modulation of Lung Inflammation in Mice.Front Immunol. 2017 Jun 9;8:658. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00658. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28649248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fang LC, Komaki R, Allen P, Guerrero T, Mohan R, Cox JD (2006) Comparison of outcomes for patients with medically inoperable Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer treated with two-dimensional vs. three-dimensional radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66: 108–116. - PubMed
-
- Bush DA, Cheek G, Zaheer S, Wallen J, Mirshahidi H, Katerelos A (2013) High-dose hypofractionated proton beam radiation therapy is safe and effective for central and peripheral early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: results of a 12-year experience at Loma Linda University Medical Center. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86: 964–968. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.05.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

