Foxc2 enhances proliferation and inhibits apoptosis through activating Akt/mTORC1 signaling pathway in mouse preadipocytes
- PMID: 26113535
- PMCID: PMC4513988
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M057679
Foxc2 enhances proliferation and inhibits apoptosis through activating Akt/mTORC1 signaling pathway in mouse preadipocytes
Abstract
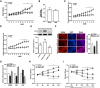
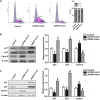
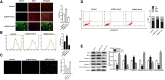
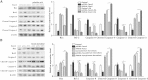
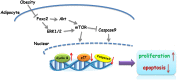
Forkhead box C2 (Foxc2) protein is a transcription factor in regulation of development, metabolism, and immunology. However, the regulatory mechanisms of Foxc2 on proliferation and apoptosis of preadipocytes are unclear. In this study, we found that high-fat-diet-induced obesity elevated the expression of Foxc2 and cyclin E after 6 weeks. Additionally, Foxc2 suppressed preadipocyte differentiation, increased cell counts and augmented G1-S transition of preadipocytes, along with the elevation of cyclin E expression and the reduction levels of p27 and p53. Furthermore, Foxc2 knockdown reduced early apoptotic cells with accompanying reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential and increased fragmentation of genomic DNA. We show that Foxc2 reduces the expression of Bax, caspase-9, and caspase-3 in both serum-starved and palmitic acid-induced cell apoptotic models, which confirms the anti-apoptotic role of Foxc2. Moreover, the protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)C1 signaling pathway and the ERK/mTORC1 signaling pathway were activated along with preadipocyte proliferation in response to Foxc2 overexpression, whereas apoptosis marker genes were downregulated during this process. Those effects were blocked by the interference of Foxc2 or signal pathways specific inhibitors. These data collectively reveal that Foxc2 enhances proliferation of preadipocytes and inhibits apoptosis of preadipocytes by activating the Akt/mTORC1 and ERK/mTORC1 signaling pathways.
Keywords: cell death; cell signaling; fat; forkhead box C2; protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin C1 signaling pathway; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fisetin regulates obesity by targeting mTORC1 signaling.J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Aug;24(8):1547-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Mar 18. J Nutr Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23517912
-
Regulated in DNA damage and development 1 (REDD1) promotes cell survival during serum deprivation by sustaining repression of signaling through the mechanistic target of rapamycin in complex 1 (mTORC1).Cell Signal. 2013 Dec;25(12):2709-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.08.038. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 24018049 Free PMC article.
-
The mTOR pathway controls cell proliferation by regulating the FoxO3a transcription factor via SGK1 kinase.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 18;9(2):e88891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088891. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24558442 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between FOXO, TOR, and Akt.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov;1813(11):1965-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.03.013. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21440577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The FOXC2 Transcription Factor: A Master Regulator of Chemoresistance in Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231155284. doi: 10.1177/15330338231155284. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36740986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Organoid Cultures to Study the Effects of Pregnancy Hormones on the Epigenome and Transcriptional Output of Mammary Epithelial Cells.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2020 Dec;25(4):351-366. doi: 10.1007/s10911-020-09465-0. Epub 2020 Nov 1. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2020. PMID: 33131024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reducing Smad3/ATF4 was essential for Sirt1 inhibiting ER stress-induced apoptosis in mice brown adipose tissue.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):9267-9279. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14035. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28030827 Free PMC article.
-
KLF7 promotes preadipocyte proliferation via activation of the Akt signaling pathway by Cis-regulating CDKN3.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Oct 25;54(10):1486-1496. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022144. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022. PMID: 36269137 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-seq Analysis of Wild-Type vs. FOXC2-Deficient Melanoma Cells Reveals a Role for the FOXC2 Transcription Factor in the Regulation of Multiple Oncogenic Pathways.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 27;10:267. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00267. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32175283 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inhibition of PKC/MEK pathway suppresses β1-integrin and mitigates breast cancer cells proliferation.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Jul 21;8:1530-1537. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.07.012. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34408972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mani S. A., Yang J., Brooks M., Schwaninger G., Zhou A., Miura N., Kutok J. L., Hartwell K., Richardson A. L., Weinberg R. A. 2007. Mesenchyme forkhead 1 (FOXC2) plays a key role in metastasis and is associated with aggressive basal-like breast cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 104: 10069–10074. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kume T., Deng K., Hogan B. 2000. Murine forkhead/winged helix genes Foxc1 (Mf1) and Foxc2 (Mfh1) are required for the early organogenesis of the kidney and urinary tract. Development. 127: 1387–1395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

