SH2-PLA: a sensitive in-solution approach for quantification of modular domain binding by proximity ligation and real-time PCR
- PMID: 26112401
- PMCID: PMC4482279
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-015-0169-1
SH2-PLA: a sensitive in-solution approach for quantification of modular domain binding by proximity ligation and real-time PCR
Abstract
Background: There is a great interest in studying phosphotyrosine dependent protein-protein interactions in tyrosine kinase pathways that play a critical role in many aspects of cellular function. We previously established SH2 profiling, a phosphoproteomic approach based on membrane binding assays that utilizes purified Src Homology 2 (SH2) domains as a molecular tool to profile the global tyrosine phosphorylation state of cells. However, in order to use this method to investigate SH2 binding sites on a specific target in cell lysate, additional procedures such as pull-down or immunoprecipitation which consume large amounts of sample are required.
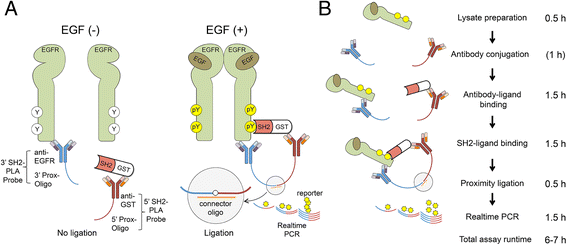
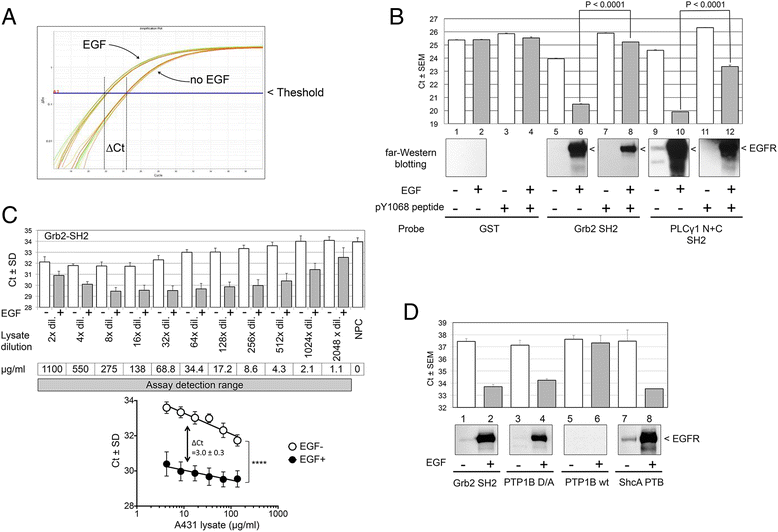
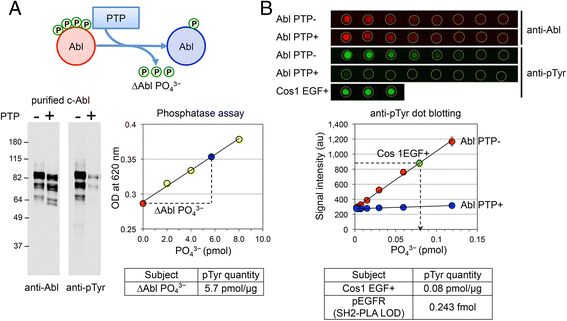
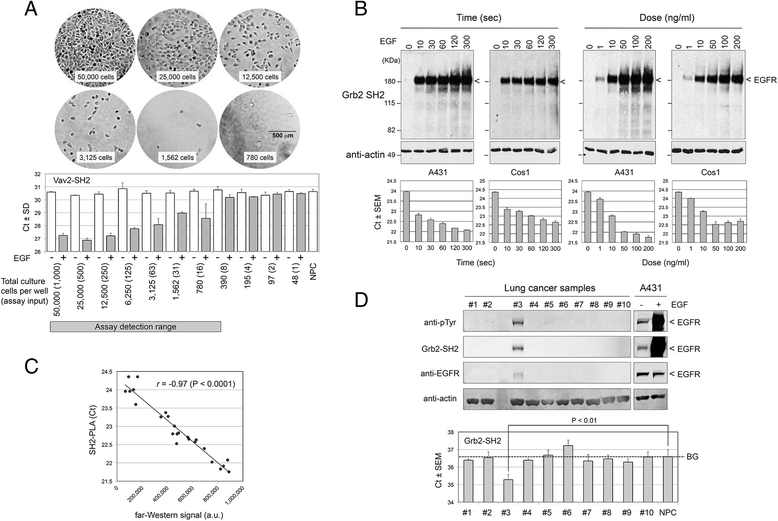
Results: We have developed PLA-SH2, an alternative in-solution modular domain binding assay that takes advantage of Proximity Ligation Assay and real-time PCR. The SH2-PLA assay utilizes oligonucleotide-conjugated anti-GST and anti-EGFR antibodies recognizing a GST-SH2 probe and cellular EGFR, respectively. If the GST-SH2 and EGFR are in close proximity as a result of SH2-phosphotyrosine interactions, the two oligonucleotides are brought within a suitable distance for ligation to occur, allowing for efficient complex amplification via real-time PCR. The assay detected signal across at least 3 orders of magnitude of lysate input with a linear range spanning 1-2 orders and a low femtomole limit of detection for EGFR phosphotyrosine. SH2 binding kinetics determined by PLA-SH2 showed good agreement with established far-Western analyses for A431 and Cos1 cells stimulated with EGF at various times and doses. Further, we showed that PLA-SH2 can survey lung cancer tissues using 1 μl lysate without requiring phospho-enrichment.
Conclusions: We showed for the first time that interactions between SH2 domain probes and EGFR in cell lysate can be determined in a microliter-scale assay using SH2-PLA. The obvious benefit of this method is that the low sample requirement allows detection of SH2 binding in samples which are difficult to analyze using traditional protein interaction assays. This feature along with short assay runtime makes this method a useful platform for the development of high throughput assays to determine modular domain-ligand interactions which could have wide-ranging applications in both basic and translational cancer research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In-Solution SH2 Domain Binding Assay Based on Proximity Ligation.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1555:331-347. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6762-9_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28092041
-
Rosette Assay: Highly Customizable Dot-Blot for SH2 Domain Screening.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1555:437-451. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6762-9_26. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28092049
-
Sensitive Approaches for the Assay of the Global Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Complex Samples Using a Mutated SH2 Domain.Anal Chem. 2017 Feb 21;89(4):2304-2311. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03812. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 28192934
-
Profiling the global tyrosine phosphorylation state.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2003 Apr;2(4):215-33. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R300002-MCP200. Epub 2003 May 17. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2003. PMID: 12754303 Review.
-
The language of SH2 domain interactions defines phosphotyrosine-mediated signal transduction.FEBS Lett. 2012 Aug 14;586(17):2597-605. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.04.054. Epub 2012 May 5. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22569091 Review.
Cited by
-
Oligomerization of MrgC11 and μ-opioid receptors in sensory neurons enhances morphine analgesia.Sci Signal. 2018 Jun 19;11(535):eaao3134. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aao3134. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 29921657 Free PMC article.
-
Current Approaches Toward Quantitative Mapping of the Interactome.Front Genet. 2016 May 4;7:74. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00074. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27200083 Free PMC article.
-
Src homology 2 domains enhance tyrosine phosphorylation in vivo by protecting binding sites in their target proteins from dephosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 12;293(2):623-637. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.794412. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29162725 Free PMC article.
-
Time-resolved multimodal analysis of Src Homology 2 (SH2) domain binding in signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases.Elife. 2016 Apr 12;5:e11835. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11835. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27071344 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

