MED30 Regulates the Proliferation and Motility of Gastric Cancer Cells
- PMID: 26110885
- PMCID: PMC4482445
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130826
MED30 Regulates the Proliferation and Motility of Gastric Cancer Cells
Abstract
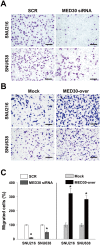
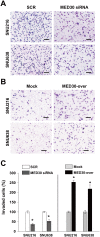
MED30 is an essential member of the mediator complex that forms a hub between transcriptional activators and RNA polymerase II. However, the expressions and roles of MED30 have been poorly characterized in cancer. In this study, we examined the functional roles of MED30 during gastric cancer progression. It was found that MED30 was overexpressed in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. Moreover, MED30 overexpression increased the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells, whereas MED30 knockdown inhibited these effects. Furthermore the knockdown significantly inhibited tumorigenicity in SCID mice. MED30 also promoted the expressions of genes related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and induced a fibroblast-like morphology. This study shows MED30 has pathophysiological roles in the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells and suggests that MED30 should be viewed as a potent therapeutic target for malignant gastric carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The knockdown of the mediator complex subunit MED30 suppresses the proliferation and migration of renal cell carcinoma cells.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018 Jun;34:18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.12.008. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29661722
-
The Contrasting Role of the Mediator Subunit MED30 in the Progression of Bladder Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2017 Dec;37(12):6685-6695. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12127. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29187445
-
Roles of DPY30 in the Proliferation and Motility of Gastric Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0131863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131863. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26147337 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and gastric cancer stem cell.Tumour Biol. 2017 May;39(5):1010428317698373. doi: 10.1177/1010428317698373. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28459211 Review.
-
The roles of mediator complex in cardiovascular diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jun;1839(6):444-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.012. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24751643 Review.
Cited by
-
Benzo(a)pyrene enhances the EMT-associated migration of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells by upregulating Twist1.Oncol Rep. 2017 Oct;38(4):2141-2147. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5874. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28791412 Free PMC article.
-
The nematode homologue of Mediator complex subunit 28, F28F8.5, is a critical regulator of C. elegans development.PeerJ. 2017 Jun 6;5:e3390. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3390. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 28603670 Free PMC article.
-
Gene signature predicting recurrence in oral squamous cell carcinoma is characterized by increased oxidative phosphorylation.Mol Oncol. 2023 Jan;17(1):134-149. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13328. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Mol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36271693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lauren P. The Two Histological Main Types of Gastric Carcinoma: Diffuse and So-Called Intestinal-Type Carcinoma. An Attempt at a Histo-Clinical Classification. Acta pathologica et microbiologica Scandinavica. 1965;64:31–49. Epub 1965/01/01. . - PubMed
-
- Pacelli F, Papa V, Caprino P, Sgadari A, Bossola M, Doglietto GB. Proximal compared with distal gastric cancer: multivariate analysis of prognostic factors. The American surgeon. 2001;67(7):697–703. Epub 2001/07/14. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

