RhoA orchestrates glycolysis for TH2 cell differentiation and allergic airway inflammation
- PMID: 26100081
- PMCID: PMC4684821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.05.004
RhoA orchestrates glycolysis for TH2 cell differentiation and allergic airway inflammation
Abstract
Background: Mitochondrial metabolism is known to be important for T-cell activation. However, its involvement in effector T-cell differentiation has just begun to gain attention. Importantly, how metabolic pathways are integrated with T-cell activation and effector cell differentiation and function remains largely unknown.
Objective: We sought to test our hypothesis that RhoA GTPase orchestrates glycolysis for TH2 cell differentiation and TH2-mediated allergic airway inflammation.
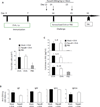
Methods: Conditional RhoA-deficient mice were generated by crossing RhoA(flox/flox) mice with CD2-Cre transgenic mice. Effects of RhoA on TH2 differentiation were evaluated based on in vitro TH2-polarized culture conditions and in vivo in ovalbumin-induced allergic airway inflammation. Cytokine levels were measured by using intracellular staining and ELISA. T-cell metabolism was measured by using the Seahorse XF24 Analyzer and flow cytometry.
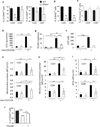
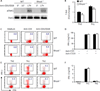
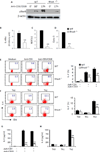
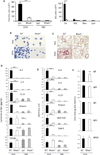
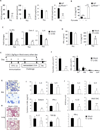
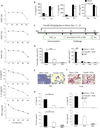
Results: Disruption of RhoA inhibited T-cell activation and TH2 differentiation in vitro and prevented the development of allergic airway inflammation in vivo, with no effect on TH1 cells. RhoA deficiency in activated T cells led to multiple defects in metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. Importantly, RhoA couples glycolysis to TH2 cell differentiation and allergic airway inflammation through regulating IL-4 receptor mRNA expression and TH2-specific signaling events. Finally, inhibition of Rho-associated protein kinase, an immediate downstream effector of RhoA, blocked TH2 differentiation and allergic airway inflammation.
Conclusion: RhoA is a key component of the signaling cascades leading to TH2 differentiation and allergic airway inflammation at least in part through control of T-cell metabolism and the Rho-associated protein kinase pathway.
Keywords: RhoA; T(H)2 differentiation; T-cell metabolism; allergic airway inflammation; glycolysis.
Copyright © 2015 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ablation of RhoA impairs Th17 cell differentiation and alleviates house dust mite-triggered allergic airway inflammation.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Nov;106(5):1139-1151. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3A0119-025RRR. Epub 2019 Jul 1. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 31260596 Free PMC article.
-
Janus kinase 1/3 signaling pathways are key initiators of TH2 differentiation and lung allergic responses.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Apr;133(4):1162-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.10.036. Epub 2013 Dec 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24365136 Free PMC article.
-
Role of IL-4 receptor α-positive CD4(+) T cells in chronic airway hyperresponsiveness.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Jun;137(6):1852-1862.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.10.036. Epub 2015 Dec 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26688514
-
Allergic airway inflammation: key players beyond the Th2 cell pathway.Immunol Rev. 2017 Jul;278(1):145-161. doi: 10.1111/imr.12540. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28658544 Review.
-
Immune Metabolism of IL-4-Activated B Cells and Th2 Cells in the Context of Allergic Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 1;12:790658. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.790658. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ras homolog family member A/Rho-associated protein kinase 1 signaling modulates lineage commitment of mesenchymal stem cells in asthmatic patients through lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Apr;143(4):1560-1574.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.08.023. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30194990 Free PMC article.
-
The Metabolic Requirements of Th2 Cell Differentiation.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 27;10:2318. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02318. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31611881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cell metabolism: new insights in systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis and therapy.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Feb;16(2):100-112. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0356-x. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31949287 Review.
-
ARHGAP4 mediates the Warburg effect in pancreatic cancer through the mTOR and HIF-1α signaling pathways.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Jun 28;12:5003-5012. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S207560. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31303760 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA G17V is sufficient to induce autoimmunity and promotes T-cell lymphomagenesis in mice.Blood. 2018 Aug 30;132(9):935-947. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-818617. Epub 2018 May 16. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29769264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowen H, Kelly A, Lee T, Lavender P. Control of cytokine gene transcription in Th1 and Th2 cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008;38:1422–1431. - PubMed
-
- Nakayama T, Yamashita M. The TCR-mediated signaling pathways that control the direction of helper T cell differentiation. Semin Immunol. 2010;22:303–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

