Cdc14 Early Anaphase Release, FEAR, Is Limited to the Nucleus and Dispensable for Efficient Mitotic Exit
- PMID: 26090959
- PMCID: PMC4474866
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128604
Cdc14 Early Anaphase Release, FEAR, Is Limited to the Nucleus and Dispensable for Efficient Mitotic Exit
Abstract
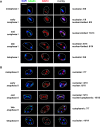
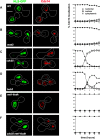
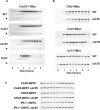
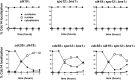
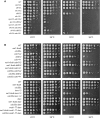
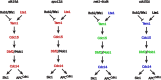
Cdc14 phosphatase is a key regulator of exit from mitosis, acting primarily through antagonism of cyclin-dependent kinase, and is also thought to be important for meiosis. Cdc14 is released from its sequestration site in the nucleolus in two stages, first by the non-essential Cdc Fourteen Early Anaphase Release (FEAR) pathway and later by the essential Mitotic Exit Network (MEN), which drives efficient export of Cdc14 to the cytoplasm. We find that Cdc14 is confined to the nucleus during early mitotic anaphase release, and during its meiosis I release. Proteins whose degradation is directed by Cdc14 as a requirement for mitotic exit (e.g. the B-type cyclin, Clb2), remain stable during mitotic FEAR, a result consistent with Cdc14 being restricted to the nucleus and not participating directly in mitotic exit. Cdc14 released by the FEAR pathway has been proposed to have a wide variety of activities, all of which are thought to promote passage through anaphase. Proposed functions of FEAR include stabilization of anaphase spindles, resolution of the rDNA to allow its segregation, and priming of the MEN so that mitotic exit can occur promptly and efficiently. We tested the model for FEAR functions using the FEAR-deficient mutation net1-6cdk. Our cytological observations indicate that, contrary to the current model, FEAR is fully dispensable for timely progression through a series of anaphase landmarks and mitotic exit, although it is required for timely rDNA segregation. The net1-6cdk mutation suppresses temperature-sensitive mutations in MEN genes, suggesting that rather than activating mitotic exit, FEAR either inhibits the MEN or has no direct effect upon it. One interpretation of this result is that FEAR delays MEN activation to ensure that rDNA segregation occurs before mitotic exit. Our findings clarify the distinction between FEAR and MEN-dependent Cdc14 activities and will help guide emerging quantitative models of this cell cycle transition.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nur1 dephosphorylation confers positive feedback to mitotic exit phosphatase activation in budding yeast.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jan 8;11(1):e1004907. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004907. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25569132 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation by cyclin B-Cdk underlies release of mitotic exit activator Cdc14 from the nucleolus.Science. 2004 Jul 23;305(5683):516-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1099402. Science. 2004. PMID: 15273393
-
Putting the brake on FEAR: Tof2 promotes the biphasic release of Cdc14 phosphatase during mitotic exit.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(1):245-55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-08-0879. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 18923139 Free PMC article.
-
At the interface between signaling and executing anaphase--Cdc14 and the FEAR network.Genes Dev. 2004 Nov 1;18(21):2581-95. doi: 10.1101/gad.1247304. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15520278 Review.
-
Complexity of mitotic exit.Cell Cycle. 2002 Sep-Oct;1(5):300-3. doi: 10.4161/cc.1.5.142. Cell Cycle. 2002. PMID: 12461287 Review.
Cited by
-
Cdc15 Phosphorylates the C-terminal Domain of RNA Polymerase II for Transcription during Mitosis.J Biol Chem. 2017 Mar 31;292(13):5507-5518. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.761056. Epub 2017 Feb 15. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28202544 Free PMC article.
-
Meiosis-Specific Functions of Kinesin Motors in Cohesin Removal and Maintenance of Chromosome Integrity in Budding Yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Mar 30;40(8):e00386-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00386-19. Print 2020 Mar 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31964755 Free PMC article.
-
Three Cdk1 sites in the kinesin-5 Cin8 catalytic domain coordinate motor localization and activity during anaphase.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Sep;74(18):3395-3412. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2523-z. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28455557 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel separase-interacting protein and candidate new securin, Eip1p, in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Sep 1;30(19):2469-2489. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-11-0696. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31411946 Free PMC article.
-
The Cdc14 Phosphatase Controls Resolution of Recombination Intermediates and Crossover Formation during Meiosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9811. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189811. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Visintin R, Craig K, Hwang ES, Prinz S, Tyers M, Amon A. The phosphatase Cdc14 triggers mitotic exit by reversal of Cdk-dependent phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 1998;2(6):709–18. . - PubMed
-
- Straight AF, Shou W, Dowd GJ, Turck CW, Deshaies RJ, Johnson AD, et al. Net1, a Sir2-associated nucleolar protein required for rDNA silencing and nucleolar integrity. Cell. 1999;97(2):245–56. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

