Single-fluorophore membrane transport activity sensors with dual-emission read-out
- PMID: 26090909
- PMCID: PMC4491562
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.07113
Single-fluorophore membrane transport activity sensors with dual-emission read-out
Abstract
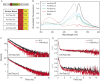
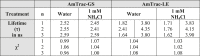
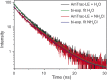
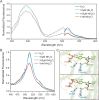
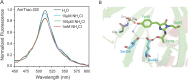
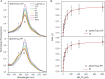
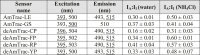
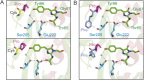
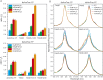
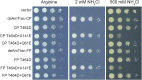
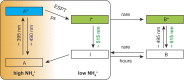
We recently described a series of genetically encoded, single-fluorophore-based sensors, termed AmTrac and MepTrac, which monitor membrane transporter activity in vivo (De Michele et al., 2013). However, being intensiometric, AmTrac and Meptrac are limited in their use for quantitative studies. Here, we characterized the photophysical properties (steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy as well as anisotropy decay analysis) of different AmTrac sensors with diverging fluorescence properties in order to generate improved, ratiometric sensors. By replacing key amino acid residues in AmTrac we constructed a set of dual-emission AmTrac sensors named deAmTracs. deAmTracs show opposing changes of blue and green emission with almost doubled emission ratio upon ammonium addition. The response ratio of the deAmTracs correlated with transport activity in mutants with altered capacity. Our results suggest that partial disruption of distance-dependent excited-state proton transfer is important for the successful generation of single-fluorophore-based dual-emission sensors.
Keywords: S. cerevisiae; biophysics; biosensor; cell biology; excited state proton transfer (ESPT); fluorescence; green fluorescent protein; structural biology; transporter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Green fluorescent protein variants as ratiometric dual emission pH sensors. 3. Temperature dependence of proton transfer.Biochemistry. 2005 Jun 21;44(24):8701-11. doi: 10.1021/bi050132a. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15952777
-
Green fluorescent protein variants as ratiometric dual emission pH sensors. 1. Structural characterization and preliminary application.Biochemistry. 2002 Dec 31;41(52):15477-88. doi: 10.1021/bi026609p. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12501176
-
Green fluorescent protein variants as ratiometric dual emission pH sensors. 2. Excited-state dynamics.Biochemistry. 2002 Dec 31;41(52):15489-94. doi: 10.1021/bi026610o. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12501177
-
Fluorescent biosensors of protein function.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2008 Feb;12(1):60-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.01.020. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2008. PMID: 18282482 Review.
-
Quantitative imaging using genetically encoded sensors for small molecules in plants.Plant J. 2012 Apr;70(1):108-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04910.x. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22449046 Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring nutrients in plants with genetically encoded sensors: achievements and perspectives.Plant Physiol. 2023 Aug 31;193(1):195-216. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad337. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37307576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiparameter in vivo imaging in plants using genetically encoded fluorescent indicator multiplexing.Plant Physiol. 2021 Oct 5;187(2):537-549. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab399. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 35237819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seeing Neurodegeneration in a New Light Using Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Biosensors and iPSCs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 16;24(2):1766. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021766. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ratiometric Matryoshka biosensors from a nested cassette of green- and orange-emitting fluorescent proteins.Nat Commun. 2017 Sep 5;8(1):431. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00400-2. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28874729 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the molecular mechanism responsible for GCaMP6m's Ca2+-dependent change in fluorescence.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 9;12(2):e0170934. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170934. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28182677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akerboom J, Rivera JD, Guilbe MM, Malavé EC, Hernandez HH, Tian L, Hires SA, Marvin JS, Looger LL, Schreiter ER. Crystal structures of the GCaMP calcium sensor reveal the mechanism of fluorescence signal change and aid rational design. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2009;284:6455–6464. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807657200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ast C, Frommer WB, Grossmann G, De Michele R. Quantification of extracellular ammonium concentrations and transporter activity in yeast using AmTrac fluorescent sensors. Bio-Protocol. 2015;5:e1372.
-
- Brejc K, Sixma TK, Kitts PA, Kain SR, Tsien RY, Ormö M, Remington SJ. Structural basis for dual excitation and photoisomerization of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA. 1997;94:2306–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2306. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

