By the company they keep: interaction networks define the binding ability of transcription factors
- PMID: 26089389
- PMCID: PMC4627061
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv607
By the company they keep: interaction networks define the binding ability of transcription factors
Abstract
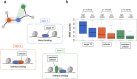
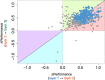
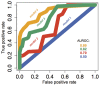
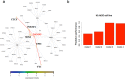
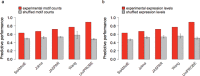
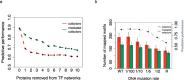
Access to genome-wide data provides the opportunity to address questions concerning the ability of transcription factors (TFs) to assemble in distinct macromolecular complexes. Here, we introduce the PAnDA (Protein And DNA Associations) approach to characterize DNA associations with human TFs using expression profiles, protein-protein interactions and recognition motifs. Our method predicts TF binding events with >0.80 accuracy revealing cell-specific regulatory patterns that can be exploited for future investigations. Even when the precise DNA-binding motifs of a specific TF are not available, the information derived from protein-protein networks is sufficient to perform high-confidence predictions (area under the ROC curve of 0.89). PAnDA is freely available at http://service.tartaglialab.com/new_submission/panda.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions.Science. 2007 Jun 8;316(5830):1497-502. doi: 10.1126/science.1141319. Epub 2007 May 31. Science. 2007. PMID: 17540862
-
Prediction of TF target sites based on atomistic models of protein-DNA complexes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Oct 16;9:436. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-436. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18922190 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative evaluation of protein-DNA interactions using an optimized knowledge-based potential.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 26;33(2):546-58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki204. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15673715 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-centered approaches to characterize regulatory protein-DNA interaction complexes.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Mar;6(3):462-8. doi: 10.1039/b916137f. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20174675 Review.
-
In vitro DNA-binding profile of transcription factors: methods and new insights.J Endocrinol. 2011 Jul;210(1):15-27. doi: 10.1530/JOE-11-0010. Epub 2011 Mar 9. J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21389103 Review.
Cited by
-
Matrix-screening reveals a vast potential for direct protein-protein interactions among RNA binding proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jul 9;49(12):6702-6721. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab490. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34133714 Free PMC article.
-
An integrative imputation method based on multi-omics datasets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun 21;17:247. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1122-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27329642 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the characterization of RNA-binding proteins.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Nov;7(6):793-810. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1378. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27503141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WSMD: weakly-supervised motif discovery in transcription factor ChIP-seq data.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 12;7(1):3217. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03554-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28607381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vaquerizas J.M., Kummerfeld S.K., Teichmann S.A., Luscombe N.M. A census of human transcription factors: function, expression and evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009;10:252–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

