The Nucleocapsid Protein of Coronaviruses Acts as a Viral Suppressor of RNA Silencing in Mammalian Cells
- PMID: 26085159
- PMCID: PMC4524063
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01331-15
The Nucleocapsid Protein of Coronaviruses Acts as a Viral Suppressor of RNA Silencing in Mammalian Cells
Abstract
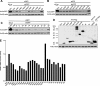
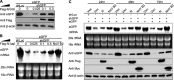
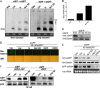
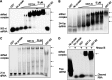
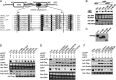
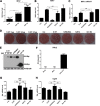
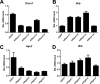
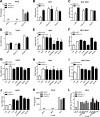
RNA interference (RNAi) is a process of eukaryotic posttranscriptional gene silencing that functions in antiviral immunity in plants, nematodes, and insects. However, recent studies provided strong supports that RNAi also plays a role in antiviral mechanism in mammalian cells. To combat RNAi-mediated antiviral responses, many viruses encode viral suppressors of RNA silencing (VSR) to facilitate their replication. VSRs have been widely studied for plant and insect viruses, but only a few have been defined for mammalian viruses currently. We identified a novel VSR from coronaviruses, a group of medically important mammalian viruses including Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), and showed that the nucleocapsid protein (N protein) of coronaviruses suppresses RNAi triggered by either short hairpin RNAs or small interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) is closely related to SARS-CoV in the family Coronaviridae and was used as a coronavirus replication model. The replication of MHV increased when the N proteins were expressed in trans, while knockdown of Dicer1 or Ago2 transcripts facilitated the MHV replication in mammalian cells. These results support the hypothesis that RNAi is a part of the antiviral immunity responses in mammalian cells. IMPORTANCE RNAi has been well known to play important antiviral roles from plants to invertebrates. However, recent studies provided strong supports that RNAi is also involved in antiviral response in mammalian cells. An important indication for RNAi-mediated antiviral activity in mammals is the fact that a number of mammalian viruses encode potent suppressors of RNA silencing. Our results demonstrate that coronavirus N protein could function as a VSR through its double-stranded RNA binding activity. Mutational analysis of N protein allowed us to find out the critical residues for the VSR activity. Using the MHV-A59 as the coronavirus replication model, we showed that ectopic expression of SARS-CoV N protein could promote MHV replication in RNAi-active cells but not in RNAi-depleted cells. These results indicate that coronaviruses encode a VSR that functions in the replication cycle and provide further evidence to support that RNAi-mediated antiviral response exists in mammalian cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism and Function of Antiviral RNA Interference in Mice.mBio. 2020 Aug 4;11(4):e03278-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03278-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32753500 Free PMC article.
-
A Kinome-Wide Small Interfering RNA Screen Identifies Proviral and Antiviral Host Factors in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication, Including Double-Stranded RNA-Activated Protein Kinase and Early Secretory Pathway Proteins.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(16):8318-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01029-15. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26041291 Free PMC article.
-
The Capsid Protein of Semliki Forest Virus Antagonizes RNA Interference in Mammalian Cells.J Virol. 2020 Jan 17;94(3):e01233-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01233-19. Print 2020 Jan 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31694940 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian viral suppressors of RNA interference.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Nov;47(11):978-988. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.05.001. Epub 2022 May 23. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35618579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Cell entry mechanism of coronaviruses: implication in their pathogenesis].Uirusu. 2006 Dec;56(2):165-71. doi: 10.2222/jsv.56.165. Uirusu. 2006. PMID: 17446665 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 29;12(1):1936. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21953-3. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33782395 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Sars-CoV-2 structural proteins and host cellular receptors: From basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2022;132:243-277. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2022.05.010. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 36088078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects for RNAi Therapy of COVID-19.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 30;8:916. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00916. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32850752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics and genomics of SARS-CoV-2: A review of the literature with the special focus on genetic diversity and SARS-CoV-2 genome detection.Genomics. 2021 Jan;113(1 Pt 2):1221-1232. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.09.059. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33007398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virulence factors in porcine coronaviruses and vaccine design.Virus Res. 2016 Dec 2;226:142-151. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27397100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parameswaran P, Sklan E, Wilkins C, Burgon T, Samuel MA, Lu R, Ansel KM, Heissmeyer V, Einav S, Jackson W, Doukas T, Paranjape S, Polacek C, FBdos Santos Jalili R, Babrzadeh F, Gharizadeh B, Grimm D, Kay M, Koike S, Sarnow P, Ronaghi M, Ding SW, Harris E, Chow M, Diamond MS, Kirkegaard K, Glenn JS, Fire AZ. 2010. Six RNA viruses and forty-one hosts: viral small RNAs and modulation of small RNA repertoires in vertebrate and invertebrate systems. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000764. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

