ERdj5 Reductase Cooperates with Protein Disulfide Isomerase To Promote Simian Virus 40 Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Translocation
- PMID: 26085143
- PMCID: PMC4524074
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00941-15
ERdj5 Reductase Cooperates with Protein Disulfide Isomerase To Promote Simian Virus 40 Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Translocation
Abstract
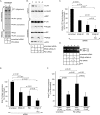
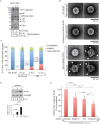
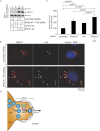
The nonenveloped polyomavirus (PyV) simian virus 40 (SV40) traffics from the cell surface to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where it penetrates the ER membrane to reach the cytosol before mobilizing into the nucleus to cause infection. Prior to ER membrane penetration, ER lumenal factors impart structural rearrangements to the virus, generating a translocation-competent virion capable of crossing the ER membrane. Here we identify ERdj5 as an ER enzyme that reduces SV40's disulfide bonds, a reaction important for its ER membrane transport and infection. ERdj5 also mediates human BK PyV infection. This enzyme cooperates with protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), a redox chaperone previously implicated in the unfolding of SV40, to fully stimulate membrane penetration. Negative-stain electron microscopy of ER-localized SV40 suggests that ERdj5 and PDI impart structural rearrangements to the virus. These conformational changes enable SV40 to engage BAP31, an ER membrane protein essential for supporting membrane penetration of the virus. Uncoupling of SV40 from BAP31 traps the virus in ER subdomains called foci, which likely serve as depots from where SV40 gains access to the cytosol. Our study thus pinpoints two ER lumenal factors that coordinately prime SV40 for ER membrane translocation and establishes a functional connection between lumenal and membrane events driving this process.
Importance: PyVs are established etiologic agents of many debilitating human diseases, especially in immunocompromised individuals. To infect cells at the cellular level, this virus family must penetrate the host ER membrane to reach the cytosol, a critical entry step. In this report, we identify two ER lumenal factors that prepare the virus for ER membrane translocation and connect these lumenal events with events on the ER membrane. Pinpointing cellular components necessary for supporting PyV infection should lead to rational therapeutic strategies for preventing and treating PyV-related diseases.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The endoplasmic reticulum membrane J protein C18 executes a distinct role in promoting simian virus 40 membrane penetration.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4058-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03574-14. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25631089 Free PMC article.
-
A nucleotide exchange factor promotes endoplasmic reticulum-to-cytosol membrane penetration of the nonenveloped virus simian virus 40.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4069-79. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03552-14. Epub 2015 Feb 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25653441 Free PMC article.
-
Bag2 Is a Component of a Cytosolic Extraction Machinery That Promotes Membrane Penetration of a Nonenveloped Virus.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00607-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00607-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29769335 Free PMC article.
-
SV40 Hijacks Cellular Transport, Membrane Penetration, and Disassembly Machineries to Promote Infection.Viruses. 2019 Oct 5;11(10):917. doi: 10.3390/v11100917. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31590347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-dependent redox reactions control endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and pathogen entry.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Apr 15;16(8):809-18. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4425. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22142231 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of the Mouse Polyomavirus Capsid Proteins with Importins Is Required for Efficient Import of Viral DNA into the Cell Nucleus.Viruses. 2018 Mar 31;10(4):165. doi: 10.3390/v10040165. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29614718 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone BiP is a master regulator of ER functions: Getting by with a little help from ERdj friends.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 8;294(6):2098-2108. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV118.002804. Epub 2018 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30563838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteostasis in Viral Infection: Unfolding the Complex Virus-Chaperone Interplay.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020 Mar 2;12(3):a034090. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034090. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020. PMID: 30858229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Disulfide Isomerases Function as the Missing Link Between Diabetes and Cancer.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Dec;37(16-18):1191-1205. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0098. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 36000195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular chaperones: from proteostasis to pathogenesis.FEBS J. 2018 Sep;285(18):3353-3361. doi: 10.1111/febs.14576. Epub 2018 Jun 22. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29890022 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

