Interleukin-35 Inhibits Endothelial Cell Activation by Suppressing MAPK-AP-1 Pathway
- PMID: 26085094
- PMCID: PMC4521049
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.663286
Interleukin-35 Inhibits Endothelial Cell Activation by Suppressing MAPK-AP-1 Pathway
Abstract
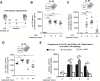
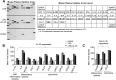
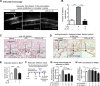
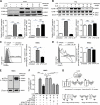
Vascular response is an essential pathological mechanism underlying various inflammatory diseases. This study determines whether IL-35, a novel responsive anti-inflammatory cytokine, inhibits vascular response in acute inflammation. Using a mouse model of LPS-induced acute inflammation and plasma samples from sepsis patients, we found that IL-35 was induced in the plasma of mice after LPS injection as well as in the plasma of sepsis patients. In addition, IL-35 decreased LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the plasma of mice. Furthermore, IL-35 inhibited leukocyte adhesion to the endothelium in the vessels of lung and cremaster muscle and decreased the numbers of inflammatory cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Mechanistically, IL-35 inhibited the LPS-induced up-regulation of endothelial cell (EC) adhesion molecule VCAM-1 through IL-35 receptors gp130 and IL-12Rβ2 via inhibition of the MAPK-activator protein-1 (AP-1) signaling pathway. We also found that IL-27, which shares the EBI3 subunit with IL-35, promoted LPS-induced VCAM-1 in human aortic ECs and that EBI3-deficient mice had similar vascular response to LPS when compared with that of WT mice. These results demonstrated for the first time that inflammation-induced IL-35 inhibits LPS-induced EC activation by suppressing MAPK-AP1-mediated VCAM-1 expression and attenuates LPS-induced secretion of proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines. Our results provide insight into the control of vascular inflammation by IL-35 and suggest that IL-35 is an attractive novel therapeutic reagent for sepsis and cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: cytokine; endothelial cell; endothelial cell activation; inflammation; interleukin-35; lipopolysaccharide (LPS); sepsis; vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1); vascular inflammation.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-35 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial cell activation by downregulating inflammation and apoptosis.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Oct 15;407(2):112784. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112784. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34508746
-
Ablation of endothelial Pfkfb3 protects mice from acute lung injury in LPS-induced endotoxemia.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Aug;146:104292. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104292. Epub 2019 Jun 2. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31167111 Free PMC article.
-
ILK mediates LPS-induced vascular adhesion receptor expression and subsequent leucocyte trans-endothelial migration.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 May 1;86(2):283-92. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq050. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20164118
-
Celecoxib attenuates interleukin 33-induced expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in human ovarian endometriotic stromal cells.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2024 Mar;63(2):178-185. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2024.01.012. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38485312 Review.
-
IL-35, as a newly proposed homeostasis-associated molecular pattern, plays three major functions including anti-inflammatory initiator, effector, and blocker in cardiovascular diseases.Cytokine. 2019 Oct;122:154076. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 28648331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Caspase-4/11 promotes hyperlipidemia and chronic kidney disease-accelerated vascular inflammation by enhancing trained immunity.JCI Insight. 2024 Jul 18;9(16):e177229. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.177229. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39024553 Free PMC article.
-
IL35 attenuated LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating macrophage polarization.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):5811-5820. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07293-5. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35748972 Free PMC article.
-
The Pathogenic Role of Oxidative Stress, Cytokine Expression, and Impaired Hematological Indices in Diabetic Cardiovascular Diseases.Inflammation. 2023 Feb;46(1):146-160. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01718-w. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 35997998 Free PMC article.
-
ROS systems are a new integrated network for sensing homeostasis and alarming stresses in organelle metabolic processes.Redox Biol. 2020 Oct;37:101696. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101696. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32950427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocyte Adhesion Assays for Detecting Endothelial Cell Activation in Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2419:169-182. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1924-7_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35237964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angus D. C., Linde-Zwirble W. T., Lidicker J., Clermont G., Carcillo J., Pinsky M. R. (2001) Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit. Care Med. 29, 1303–1310 - PubMed
-
- Wood K. A., Angus D. C. (2004) Pharmacoeconomic implications of new therapies in sepsis. PharmacoEconomics 22, 895–906 - PubMed
-
- Stoll L. L., Denning G. M., Weintraub N. L. (2004) Potential role of endotoxin as a proinflammatory mediator of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24, 2227–2236 - PubMed
-
- Ait-Oufella H., Salomon B. L., Potteaux S., Robertson A. K., Gourdy P., Zoll J., Merval R., Esposito B., Cohen J. L., Fisson S., Flavell R. A., Hansson G. K., Klatzmann D., Tedgui A., Mallat Z. (2006) Natural regulatory T cells control the development of atherosclerosis in mice. Nat. Med. 12, 178–180 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

