Developmental pluripotency-associated 4: a novel predictor for prognosis and a potential therapeutic target for colon cancer
- PMID: 26063247
- PMCID: PMC4466839
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-015-0176-z
Developmental pluripotency-associated 4: a novel predictor for prognosis and a potential therapeutic target for colon cancer
Abstract
Backgrounds: Developmental pluripotency-associated 4 (Dppa4) gene plays an important role in self-renewal and pluripotency sustainability in embryonic stem cells. It is re-expressed in several malignant tumors and is identified as a new pluripotency-related oncogene. The present study investigates the expression and clinical significance of Dppa4 in colon cancer.
Methods: Real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting were used to evaluate Dppa4 mRNA and protein expression in 39 pairs of fresh-frozzen colon cancer samples, which were compared with adjacent normal mucosa. The Dppa4 protein was evaluated by immunohistochemical techniques using colon tissue microarrays (TMA). The sample included 185 cancer specimens and corresponding normal colorectal mucosa. The effect of Dppa4 knockdown on colorectal cancer cell proliferation was investigated using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) assays and colony-formation assays.
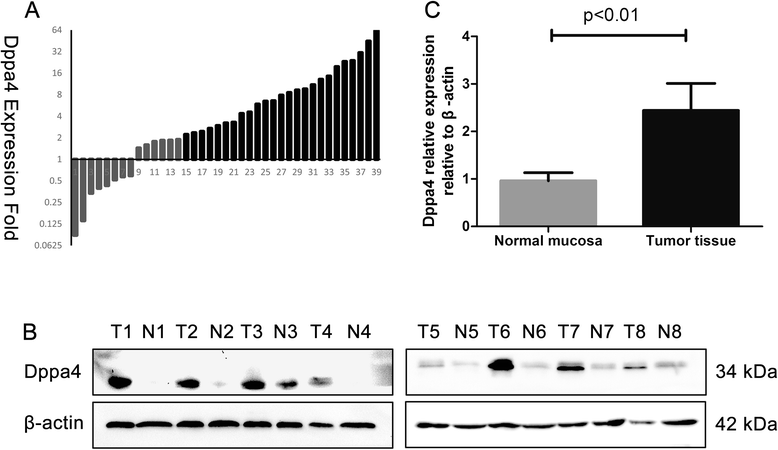
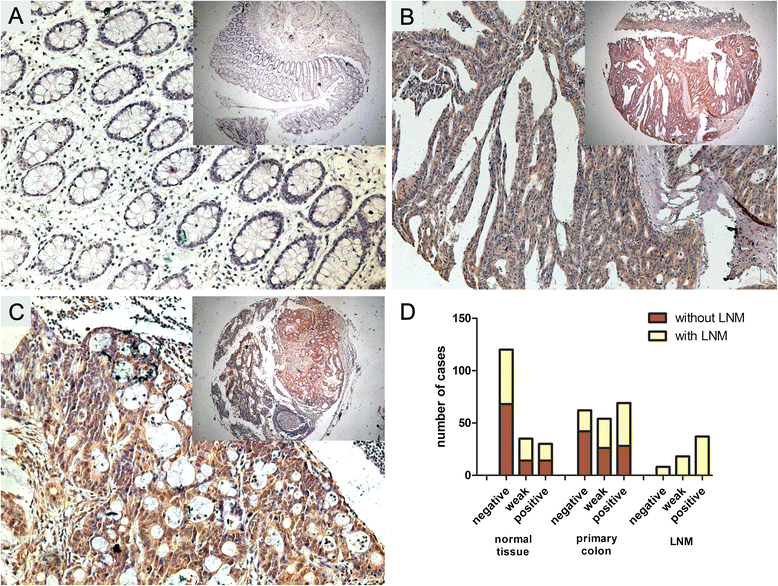
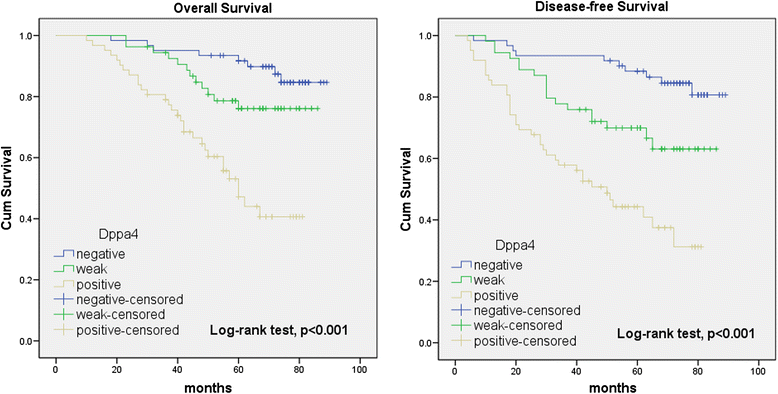
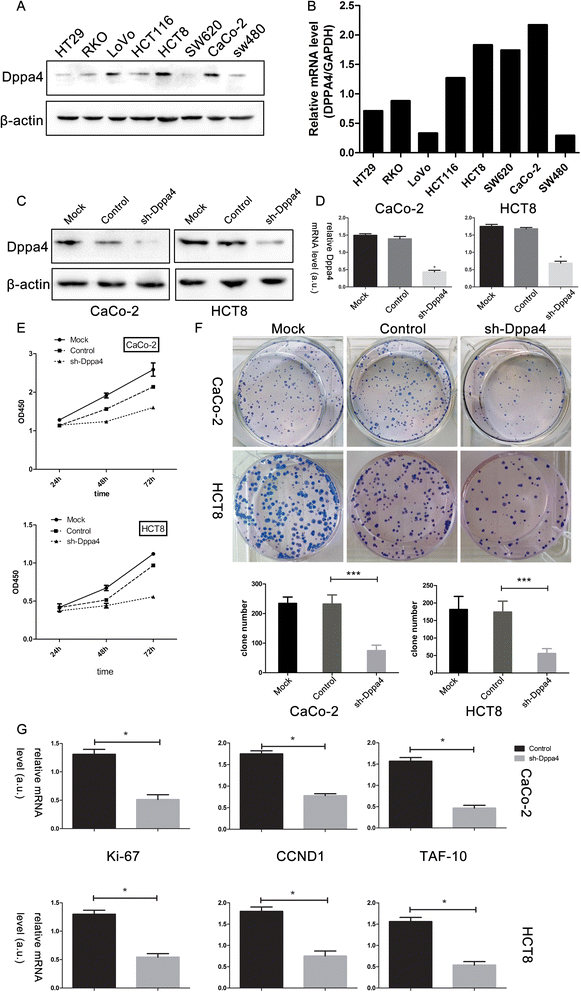
Results: Both the mRNA and protein level expression of Dppa4 gene was found to be upregulated in colon cancer tissues. Furthermore, the upregulated expression of Dppa4 was significantly correlated with the results of American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage (P = 0.01), invasion depth (P = 0.028), nodal involvement (P = 0.012), distant metastasis (P = 0.003), and differentiation (P = 0.002). Dppa4 was also shown to be an independent prognostic indicator of disease-free survival (HR 6.118, 95 % CI 3.004-12.462) and overall survival (HR 6.348, 95 % CI 2.875-14.014) for patients with colon cancer. Knockdown of Dppa4 expression inhibited the proliferation of colorectal cancer cell lines through G1/S transition regulation.
Conclusion: The results indicate that Dppa4 might play an important role in colon cancer progression and function as a novel prognostic indicator and a potential therapeutic target.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DPPA2, DPPA4, and other DPPA factor epigenomic functions in cell fate and cancer.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Dec 14;16(12):2844-2851. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.10.008. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 34767751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Karyopherin alpha 2 is a novel prognostic marker and a potential therapeutic target for colon cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 1;34:145. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0261-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26626145 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of LARP1 predicts poor prognosis of colorectal cancer and is expected to be a potential therapeutic target.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):14585-14594. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5332-3. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27614686 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 2 is a predictor of survival and a potential therapeutic target in colon cancer.Oncol Rep. 2014 Apr;31(4):1802-10. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3035. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24573556
-
Msi-1 is a predictor of survival and a novel therapeutic target in colon cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2011 Jul;18(7):2074-83. doi: 10.1245/s10434-011-1567-9. Epub 2011 Mar 26. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21442350
Cited by
-
Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein is a prognostic factor and biomarker of colon cancer and promotes cell proliferation by activating the Akt pathway.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Jun;144(6):1049-1063. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2626-4. Epub 2018 Mar 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29560517
-
Bivalent chromatin: a developmental balancing act tipped in cancer.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Feb 28;52(1):217-229. doi: 10.1042/BST20230426. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38385532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) infection on bovine mammary epithelial cells RNA-seq transcriptome profile.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 24;15(6):e0234939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234939. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32579585 Free PMC article.
-
DPPA2, DPPA4, and other DPPA factor epigenomic functions in cell fate and cancer.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Dec 14;16(12):2844-2851. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.10.008. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 34767751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OTUB2 regulates KRT80 stability via deubiquitination and promotes tumour proliferation in gastric cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Feb 2;8(1):45. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00839-3. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35110531 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

