Targeting of anti-citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis using peptides mimicking endogenously citrullinated fibrinogen antigens
- PMID: 26059223
- PMCID: PMC4484629
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0666-6
Targeting of anti-citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis using peptides mimicking endogenously citrullinated fibrinogen antigens
Abstract
Introduction: We have previously identified endogenously citrullinated peptides derived from fibrinogen in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial tissues. In this study, we have investigated the auto-antigenicity of four of those citrullinated peptides, and explored their feasibility to target anti-citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies (ACPA).
Methods: The autoantigenic potential of the fibrinogen peptides was investigated by screening 927 serum samples from the Epidemiological Investigation of RA (EIRA) cohort on a peptide microarray based on the ImmunoCAP ISAC® system. In order to assay for ACPA blocking, two independent pools of purified ACPA were incubated with the respective targeting peptide prior to binding to cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP)2 using the CCPlus® ELISA kit.
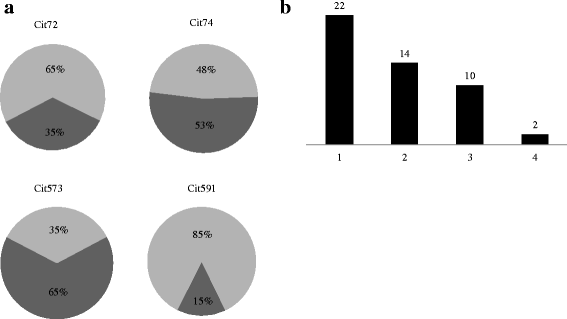
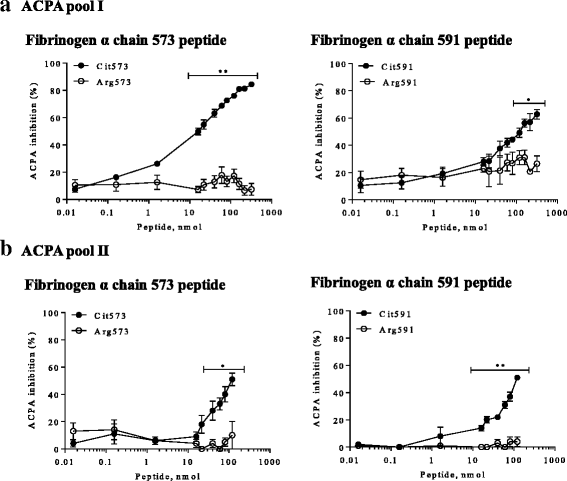
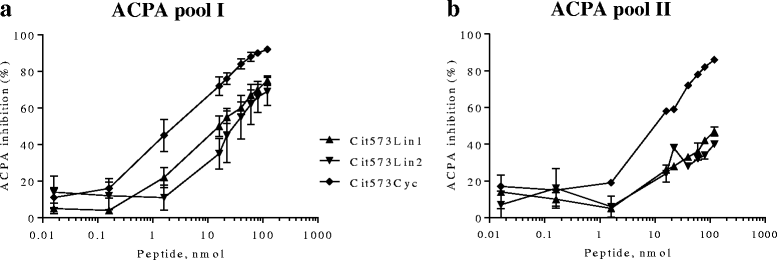
Results: Two peptides derived from the fibrinogen α chain, Arg573Cit (563-583) and Arg591Cit (580-600), referred to as Cit573 and Cit591, and two peptides from the fibrinogen β chain, Arg72Cit (62-81) and Arg74Cit (62-81) (Cit72 and Cit74), displayed 65%, 15%, 35%, and 53% of immune reactivity among CCP2-positive RA sera, respectively. In CCP2-negative RA sera, a positive reactivity was detected in 5% (Cit573), 6% (Cit591), 8% (Cit72), and 4% (Cit74). In the competition assay, Cit573 and Cit591 peptides reduced ACPA binding to CCP2 by a maximum of 84% and 63% respectively. An additive effect was observed when these peptides were combined. In contrast, Cit74 and Cit72 were less effective. Cyclization of the peptide structure containing Cit573 significantly increased the blocking efficiency.
Conclusions: Here we demonstrate extensive autoantibody reactivity against in vivo citrullinated fibrinogen epitopes, and further show the potential use of these peptides for antagonizing ACPA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The fibrin-derived citrullinated peptide β60-74Cit₆₀,₇₂,₇₄ bears the major ACPA epitope recognised by the rheumatoid arthritis-specific anticitrullinated fibrinogen autoantibodies and anti-CCP2 antibodies.Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Jun;73(6):1246-52. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202868. Epub 2013 May 1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 23636655
-
Antibody responses to de novo identified citrullinated fibrinogen peptides in rheumatoid arthritis and visualization of the corresponding B cells.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Dec 1;18(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1181-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27906052 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity purified anti-citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies target antigens expressed in the rheumatoid joint.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Aug 12;16(4):R167. doi: 10.1186/ar4683. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25112157 Free PMC article.
-
Citrullinated peptide and its relevance to rheumatoid arthritis: an update.Int J Rheum Dis. 2010 Oct;13(4):284-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2010.01553.x. Int J Rheum Dis. 2010. PMID: 21199462 Review.
-
Anti-citrullinated peptides as autoantigens in rheumatoid arthritis-relevance to treatment.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Nov;13(11):1114-20. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.08.012. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 25182207 Review.
Cited by
-
Epitope Specificity of Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies.Antibodies (Basel). 2017 Mar 8;6(1):5. doi: 10.3390/antib6010005. Antibodies (Basel). 2017. PMID: 31548521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between Anti-Citrullinated Fibrinogen Antibodies and Coronary Artery Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 Jul;70(7):1113-1117. doi: 10.1002/acr.23444. Epub 2018 May 19. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 28992379 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the Spectrum of Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody Fine Specificities Between Malaysian and Swedish Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications for Disease Pathogenesis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Jan;69(1):58-69. doi: 10.1002/art.39827. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27483449 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-citrullinated Protein Antibody Generation, Pathogenesis, Clinical Application, and Prospects.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 12;8:802934. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.802934. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35096892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibodies against citrullinated peptides are associated with clinical and radiological outcomes in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective longitudinal inception cohort study.RMD Open. 2019 Sep 3;5(2):e000946. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2019-000946. eCollection 2019. RMD Open. 2019. PMID: 31565241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC, et al. The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:155–63. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<155::AID-ANR20>3.0.CO;2-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Masson-Bessiere C, Sebbag M, Girbal-Neuhauser E, Nogueira L, Vincent C, Senshu T, et al. The major synovial targets of the rheumatoid arthritis-specific antifilaggrin autoantibodies are deiminated forms of the alpha- and beta-chains of fibrin. J Immunol. 2001;166:4177–84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.6.4177. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

