Control of mRNA Stability in Fungi by NMD, EJC and CBC Factors Through 3'UTR Introns
- PMID: 26048019
- PMCID: PMC4574236
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.115.176743
Control of mRNA Stability in Fungi by NMD, EJC and CBC Factors Through 3'UTR Introns
Abstract
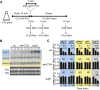
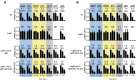
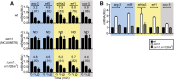
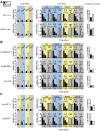
In higher eukaryotes the accelerated degradation of mRNAs harboring premature termination codons is controlled by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), exon junction complex (EJC), and nuclear cap-binding complex (CBC) factors, but the mechanistic basis for this quality-control system and the specific roles of the individual factors remain unclear. Using Neurospora crassa as a model system, we analyzed the mechanisms by which NMD is induced by spliced 3'-UTR introns or upstream open reading frames and observed that the former requires NMD, EJC, and CBC factors whereas the latter requires only the NMD factors. The transcripts for EJC components eIF4A3 and Y14, and translation termination factor eRF1, contain spliced 3'-UTR introns and each was stabilized in NMD, EJC, and CBC mutants. Reporter mRNAs containing spliced 3'-UTR introns, but not matched intronless controls, were stabilized in these mutants and were enriched in mRNPs immunopurified from wild-type cells with antibody directed against human Y14, demonstrating a direct role for spliced 3'-UTR introns in triggering EJC-mediated NMD. These results demonstrate conclusively that NMD, EJC, and CBC factors have essential roles in controlling mRNA stability and that, based on differential requirements for these factors, there are branched mechanisms for NMD. They demonstrate for the first time autoregulatory control of expression at the level of mRNA stability through the EJC/CBC branch of NMD for EJC core components, eIF4A3 and Y14, and for eRF1, which recognizes termination codons. Finally, these results show that EJC-mediated NMD occurs in fungi and thus is an evolutionarily conserved quality-control mechanism.
Keywords: Neurospora crassa; RNA stability; cap-binding complex (CBC); exon junction complex (EJC); nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD); post-transcriptional control; ribosome; spliced 3′-UTR intron; translation.
Copyright © 2015 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of the translation termination factor eRF1 is autoregulated by translational readthrough and 3'UTR intron-mediated NMD in Neurospora crassa.FEBS Lett. 2020 Nov;594(21):3504-3517. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13918. Epub 2020 Sep 12. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 32869294
-
Plant nonsense-mediated mRNA decay is controlled by different autoregulatory circuits and can be induced by an EJC-like complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jul;41(13):6715-28. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt366. Epub 2013 May 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23666629 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish rbm8a and magoh mutants reveal EJC developmental functions and new 3'UTR intron-containing NMD targets.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jun 5;16(6):e1008830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008830. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32502192 Free PMC article.
-
The long and short of EJC-independent nonsense-mediated RNA decay.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Jun 28;51(3):1121-1129. doi: 10.1042/BST20221131. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37145092 Review.
-
CBP80-promoted mRNP rearrangements during the pioneer round of translation, nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, and thereafter.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:127-34. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2010.75.028. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010. PMID: 21447822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NCBP3: A Multifaceted Adaptive Regulator of Gene Expression.Trends Biochem Sci. 2021 Feb;46(2):87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.09.003. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021. PMID: 33032857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Fungal Genomes Reveals Commonalities of Intron Gain or Loss and Functions in Intron-Poor Species.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Sep 27;38(10):4166-4186. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab094. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33772558 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the translating Neurospora ribosome arrested by cycloheximide.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Nov 30;118(48):e2111862118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2111862118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34815343 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the eRF1 translation termination factor is controlled by an autoregulatory circuit involving readthrough and nonsense-mediated decay in plants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Apr 20;45(7):4174-4188. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1303. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28062855 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved Upstream Open Reading Frame Nascent Peptides That Control Translation.Annu Rev Genet. 2020 Nov 23;54:237-264. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-112618-043822. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Annu Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32870728 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amrani N., Ganesan R., Kervestin S., Mangus D. A., Ghosh S., et al. , 2004. A faux 3′-UTR promotes aberrant termination and triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nature 432: 112–118. - PubMed
-
- Amrani N., Sachs M. S., Jacobson A., 2006. Early nonsense: mRNA decay solves a translational problem. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7: 415–425. - PubMed
-
- Bardiya N., Shiu P. K., 2007. Cyclosporin A-resistance based gene placement system for Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet. Biol. 44: 307–314. - PubMed
-
- Beelman C. A., Parker R., 1994. Differential effects of translational inhibition in cis and in trans on the decay of the unstable yeast MFA2 mRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 9687–9692. - PubMed
-
- Bicknell A. A., Cenik C., Chua H. N., Roth F. P., Moore M. J., 2012. Introns in UTRs: why we should stop ignoring them. BioEssays 34: 1025–1034. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

