Evaluation of miR-29c inhibits endotheliocyte migration and angiogenesis of human endothelial cells by suppressing the insulin like growth factor 1
- PMID: 26045889
- PMCID: PMC4448189
Evaluation of miR-29c inhibits endotheliocyte migration and angiogenesis of human endothelial cells by suppressing the insulin like growth factor 1
Abstract
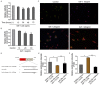
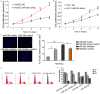
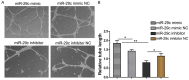
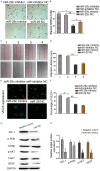
MicroRNAs, a class of 22-nucleotide non-coding RNAs, modulate gene expression by associating with the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTRs) of messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Although multiple miRNAs are known to be regulated during angiogenesis, their individual roles in blood vessel development are still not fully understood. Herein, we investigate the role of miR-29c in regulating cell cycle and angiogenic phenotype of endothelial cells. The results showed that IGF-1 is highly expressed and down-regulated by miR-29c in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Consistent with this preliminary finding, introduction of exogenous miR-29c or miR-29c inhibitor alters cell cycle progression, proliferation and tube formation of HUVEC, respectively. Furthermore, by using luciferase reporter assay, we find that the expression of IGF-1, a suppressor transcription factor, is directly regulated by miR-29c through 3'-UTR. In addition, we show that the selective inhibition of PI3K/AKT pathway prior to miR-29c stimulation prevents the expression of angiogenesis suppressor miRNAs that are family and cluster specific. As a conclusion, we find that miR-29c plays a significant role in regulating cell cycle, proliferation and angiogenic properties of HUVECs. This function is likely mediated through IGF-1 proteins at the post-transcriptional level. As a novel molecular target, miR-29c may have a potential value in the treatment of angiogenesis-associated diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases and cancers.
Keywords: IGF-1; angiogenesis; endothelial cell; miRNA-29c.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of miR-29c inhibits endotheliocyte migration and angiogenesis of human endothelial cells by suppressing the insulin like growth factor 1.Am J Transl Res. 2015 May 15;7(5):866-77. eCollection 2015. Am J Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 26175848 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-29a modulates the angiogenic properties of human endothelial cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Apr 26;434(1):143-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.03.054. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23541945 Free PMC article.
-
miR-29c inhibits metastasis of gastric cancer cells by targeting VEGFA.J Cancer. 2022 Oct 31;13(14):3566-3574. doi: 10.7150/jca.77727. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36484007 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
MiRNA-29: a microRNA family with tumor-suppressing and immune-modulating properties.Curr Mol Med. 2013 May;13(4):572-85. doi: 10.2174/1566524011313040009. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 22934851 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-29c alleviates hyperglycemia-induced inflammation via targeting TGF-β in cardiomyocytes.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Aug;479(8):2047-2054. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04813-0. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37589861
-
miR‑29 mediates exercise‑induced skeletal muscle angiogenesis by targeting VEGFA, COL4A1 and COL4A2 via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Aug;22(2):661-670. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11164. Epub 2020 May 20. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32467996 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Citrullination Represses MicroRNA Expression, Resulting in Increased Oncogene mRNAs in Somatolactotrope Cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Sep 14;38(19):e00084-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00084-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29987187 Free PMC article.
-
Preeclampsia Downregulates MicroRNAs in Fetal Endothelial Cells: Roles of miR-29a/c-3p in Endothelial Function.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Sep 1;102(9):3470-3479. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00849. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28911139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao Y, Ransom JF, Li A, Vedantham V, von Drehle M, Muth AN, Tsuchihashi T, McManus MT, Schwartz RJ, Srivastava D. Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell. 2007;129:303–317. - PubMed
-
- Wu YH, Hu TF, Chen YC, Tsai YN, Tsai YH, Cheng CC, Wang HW. The manipulation of miRNA-gene regulatory networks by KSHV induces endothelial cell motility. Blood. 2011;118:2896–2905. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
