Use of autoantigen-loaded phosphatidylserine-liposomes to arrest autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 26039878
- PMCID: PMC4454589
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127057
Use of autoantigen-loaded phosphatidylserine-liposomes to arrest autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: The development of new therapies to induce self-tolerance has been an important medical health challenge in type 1 diabetes. An ideal immunotherapy should inhibit the autoimmune attack, avoid systemic side effects and allow β-cell regeneration. Based on the immunomodulatory effects of apoptosis, we hypothesized that apoptotic mimicry can help to restore tolerance lost in autoimmune diabetes.
Objective: To generate a synthetic antigen-specific immunotherapy based on apoptosis features to specifically reestablish tolerance to β-cells in type 1 diabetes.
Methods: A central event on the surface of apoptotic cells is the exposure of phosphatidylserine, which provides the main signal for efferocytosis. Therefore, phosphatidylserine-liposomes loaded with insulin peptides were generated to simulate apoptotic cells recognition by antigen presenting cells. The effect of antigen-specific phosphatidylserine-liposomes in the reestablishment of peripheral tolerance was assessed in NOD mice, the spontaneous model of autoimmune diabetes. MHC class II-peptide tetramers were used to analyze the T cell specific response after treatment with phosphatidylserine-liposomes loaded with peptides.
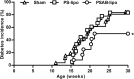
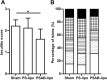
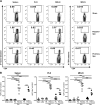
Results: We have shown that phosphatidylserine-liposomes loaded with insulin peptides induce tolerogenic dendritic cells and impair autoreactive T cell proliferation. When administered to NOD mice, liposome signal was detected in the pancreas and draining lymph nodes. This immunotherapy arrests the autoimmune aggression, reduces the severity of insulitis and prevents type 1 diabetes by apoptotic mimicry. MHC class II tetramer analysis showed that peptide-loaded phosphatidylserine-liposomes expand antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in vivo. The administration of phosphatidylserine-free liposomes emphasizes the importance of phosphatidylserine in the modulation of antigen-specific CD4+ T cell expansion.
Conclusions: We conclude that this innovative immunotherapy based on the use of liposomes constitutes a promising strategy for autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylserine-Liposomes Promote Tolerogenic Features on Dendritic Cells in Human Type 1 Diabetes by Apoptotic Mimicry.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 14;9:253. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00253. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29491866 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T Cells Induced by Single-Peptide Liposome Immunotherapy Suppress Islet-Specific T Cell Responses to Multiple Antigens and Protect from Autoimmune Diabetes.J Immunol. 2020 Apr 1;204(7):1787-1797. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901128. Epub 2020 Feb 28. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32111734 Free PMC article.
-
Liposome-based immunotherapy against autoimmune diseases: therapeutic effect on multiple sclerosis.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017 Jun;12(11):1231-1242. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2016-0410. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28593827
-
How apoptotic β-cells direct immune response to tolerance or to autoimmune diabetes: a review.Apoptosis. 2015 Mar;20(3):263-72. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1090-8. Apoptosis. 2015. PMID: 25604067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoimmune diabetes: the role of T cells, MHC molecules and autoantigens.Autoimmunity. 1998;27(3):159-77. doi: 10.3109/08916939809003864. Autoimmunity. 1998. PMID: 9609134 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 4;9(1):263. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01952-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39362875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current advances in using tolerogenic dendritic cells as a therapeutic alternative in the treatment of type 1 diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2021 May 15;12(5):603-615. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.603. World J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33995848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric micro- and nanoparticles for immune modulation.Biomater Sci. 2018 Dec 18;7(1):14-30. doi: 10.1039/c8bm01285g. Biomater Sci. 2018. PMID: 30418444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-Microparticle Platforms in Developing Next-Generation Vaccines.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jun 5;9(6):606. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9060606. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34198865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunologically Inert Nanostructures as Selective Therapeutic Tools in Inflammatory Diseases.Cells. 2021 Mar 23;10(3):707. doi: 10.3390/cells10030707. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33806746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

