Association of Antibodies to Interferon-Inducible Protein-16 With Markers of More Severe Disease in Primary Sjögren's Syndrome
- PMID: 26037655
- PMCID: PMC4847427
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.22632
Association of Antibodies to Interferon-Inducible Protein-16 With Markers of More Severe Disease in Primary Sjögren's Syndrome
Abstract
Objective: Interferon-inducible protein-16 (IFI16) is an intracellular DNA receptor involved in innate immunity. We evaluated the frequency, phenotypic characteristics, and clinical associations of anti-IFI16 antibodies in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (SS), and quantitated expression levels of IFI16 in SS and control salivary gland lysates.
Methods: Anti-IFI16 antibodies were assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using sera from patients with primary SS (n = 133) and from healthy controls (n = 47). Sera from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients (n = 132) were included as disease controls. Immunoprecipitation of in vitro transcription-translated IFI16 was used to determine which portion of IFI16 the antibodies recognized. Expression of IFI16 in salivary gland lysates was quantitated by immunoblotting.
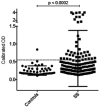
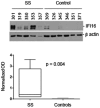
Results: Anti-IFI16 antibodies were present in the sera of 38 of 133 SS patients (29%) compared to 1 of 47 healthy controls (2.1%) (SS versus controls; P < 0.0002) and in 31 of 132 SLE controls (24%). In SS, anti-IFI16 antibodies were associated with an abnormal Schirmer's test (P = 0.003), hyperglobulinemia (P = 0.02), antinuclear antibody ≥1:320 (P = 0.01), germinal center-like structures in labial salivary gland lymphoid infiltrates (P = 0.01), and higher focus scores (3.4 versus 2.4; P = 0.005). High-titer IFI16 antibodies were directed against an epitope outside the N-terminus in 9 of 13 SS patients (69%). IFI16 was expressed in 4 of 5 (80%) of SS and 1 of 6 (17%) of control labial salivary glands.
Conclusion: Anti-IFI16 antibodies are a prominent specificity in primary SS and are associated with markers of severe disease. IFI16 is expressed at higher levels in SS salivary glands compared to controls. These high levels in disease target tissue may contribute to the ongoing anti-IFI16 immune response.
© 2016, American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Relevance of Interferon-Inducible Protein-16 Rather than Anti-Interferon-Inducible Protein-16 Autoantibodies as a Clinical and Pathogenic Biomarker in Primary Sjögren's Syndrome: Comment on the Article by Baer et al.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017 Mar;69(3):453-454. doi: 10.1002/acr.22918. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 27111652 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017 Mar;69(3):454. doi: 10.1002/acr.22917. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 27159877 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
IFI16 filament formation in salivary epithelial cells shapes the anti-IFI16 immune response in Sjögren's syndrome.JCI Insight. 2018 Sep 20;3(18):e120179. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.120179. eCollection 2018 Sep 20. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30232276 Free PMC article.
-
A novel autoantigen to differentiate limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis from diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: the interferon-inducible gene IFI16.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Dec;54(12):3939-44. doi: 10.1002/art.22266. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 17133607
-
Interferon gamma-inducible protein 16 (IFI16) and anti-IFI16 antibodies in primary Sjögren's syndrome: findings in serum and minor salivary glands.Reumatismo. 2015 Dec 30;67(3):85-90. doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2015.839. Reumatismo. 2015. PMID: 26876186
-
Clinical utility of circulating anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits NR2A/B antibody for the diagnosis of neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren's syndrome: An updated meta-analysis.Autoimmun Rev. 2017 Feb;16(2):114-122. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.12.002. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Autoimmun Rev. 2017. PMID: 27988431 Review.
-
[Isotypes and subtypes of anti-SS-A and/or SS-B antibodies in different subgroups of Sjögren's syndrome].Nihon Rinsho. 1995 Oct;53(10):2429-33. Nihon Rinsho. 1995. PMID: 8531350 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Subgroups of Sjögren's syndrome patients categorised by serological profiles: clinical and immunological characteristics.Reumatologia. 2018;56(6):346-353. doi: 10.5114/reum.2018.80711. Epub 2018 Dec 23. Reumatologia. 2018. PMID: 30647480 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in Correlation with Gene Expression Levels between Ifi200 Family Genes and Four Sets of Immune Disease-Relevant Genes.J Immunol Res. 2018 Aug 28;2018:1290814. doi: 10.1155/2018/1290814. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30246031 Free PMC article.
-
Design principles for inflammasome inhibition by pyrin-only-proteins.Elife. 2024 Jan 22;13:e81918. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81918. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38252125 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and Immune Regulation Mechanisms of PYHIN Family During Microbial Infection.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 25;12:809412. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.809412. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35145495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoantibodies in Sjögren's syndrome and its classification criteria.J Transl Autoimmun. 2021 Dec 27;5:100138. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100138. eCollection 2022. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 35024595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mondini M, Costa S, Sponza S, Gugliesi F, Gariglio M, Landolfo S. The interferon-inducible HIN-200 gene family in apoptosis and inflammation: implication for autoimmunity. Autoimmunity. 2010 Apr;43(3):226–31. - PubMed
-
- Seelig HP, Ehrfeld H, Renz M. Interferon-gamma-inducible protein p16. A new target of antinuclear antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Nov;37(11):1672–83. - PubMed
-
- Mondini M, Vidali M, De Andrea M, Azzimonti B, Airo P, D'Ambrosio R, et al. A novel autoantigen to differentiate limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis from diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: the interferon-inducible gene IFI16. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Dec;54(12):3939–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR044684/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300057C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012354/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R56A062615/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069572/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AR-053503/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053503/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AR062615/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN26S201300057C/PHS HHS/United States
- AR-43727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DE12354-15A1/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

