The role of Syk signaling in antifungal innate immunity of human corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 26036769
- PMCID: PMC4451931
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-015-0041-z
The role of Syk signaling in antifungal innate immunity of human corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Fungal keratitis is a kind of intractable and sight-threatening diseases. Spleen-tyrosine kinase (Syk) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, which plays an important role in the signaling pathway of the receptors. In the current study, we investigate the expression and function of Syk in human corneal epithelial cells with Aspergillus fumigatus (A. fumigatus) infection.
Methods: Cultured telomerase-immortalized human corneal epithelial cells (THCEs) were treated with A. fumigatus hyphae with or without treatment of Syk inhibitors. Activation of Syk and the role of Syk in regulating inflammatory cytokines and chemokines expression were evaluated. The mRNA expression was determined by real time PCR, and protein activation was measured by western blotting.
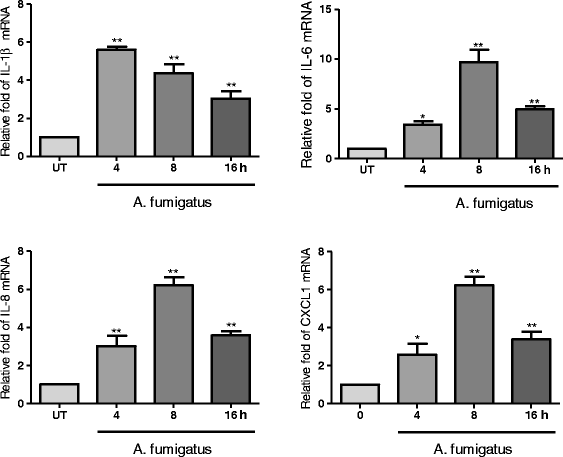
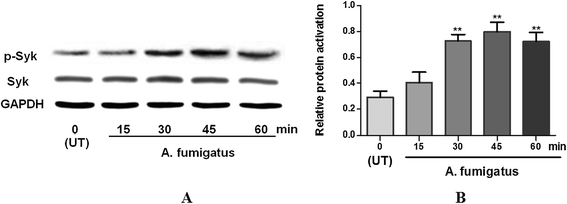
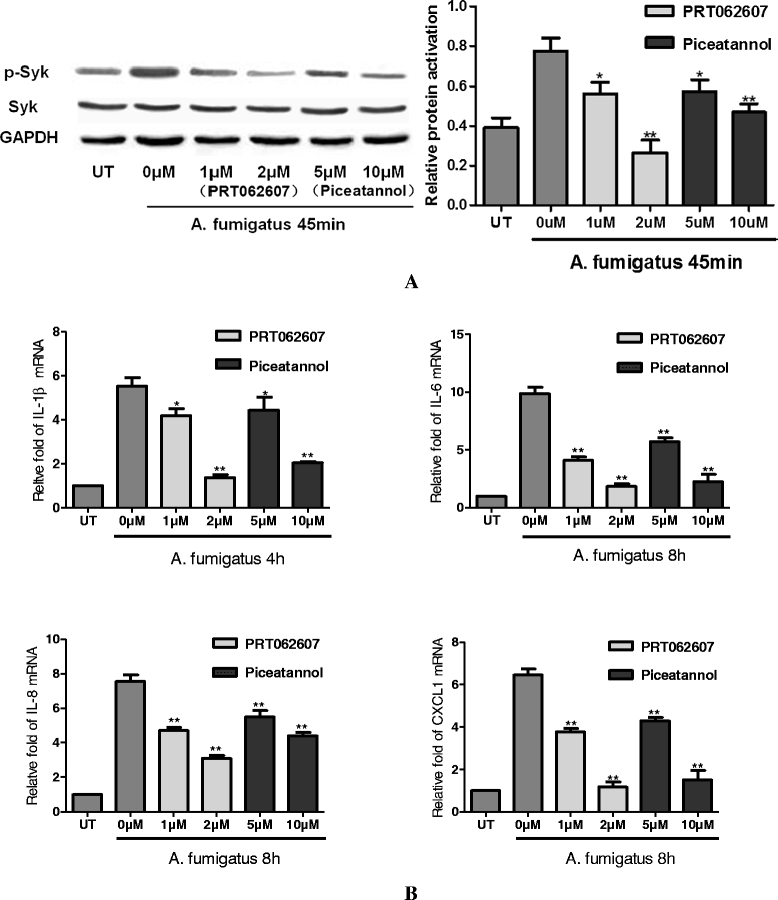
Results: Syk protein was detected in THCEs, and its activation was enhanced after treatment of A. fumigatus hyphae. Expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and IL-6) and chemokines (IL-8 and CXCL1) mRNA were significantly increased after stimulation of A. fumigatus hyphae in THCEs. Activation of Syk and expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and CXCL1 by A. fumigatus hyphae were blocked by Syk inhibitors.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that normal human corneal epithelial cells produce Syk, and Syk activation plays an important role in regulating A. fumigatus hyphae-induced inflammatory responses in THCEs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phospholipase Cγ2 is critical for Ca2+ flux and cytokine production in anti-fungal innate immunity of human corneal epithelial cells.BMC Ophthalmol. 2018 Jul 13;18(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12886-018-0847-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 30005593 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NF-κB and respiratory burst following Aspergillus fumigatus stimulation of macrophages.Immunobiology. 2014 Jan;219(1):25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Immunobiology. 2014. PMID: 23886693
-
Role of PTX3 in corneal epithelial innate immunity against Aspergillus fumigatus infection.Exp Eye Res. 2018 Feb;167:152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.11.017. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Exp Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 27889356
-
Syk: a novel target for treatment of inflammation in lung disease.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009 Jun;8(2):87-95. doi: 10.2174/187152809788462626. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19530990 Review.
-
Functional roles of Syk in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:270302. doi: 10.1155/2014/270302. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 25045209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review of clinical and basic approaches of fungal keratitis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2016 Nov 18;9(11):1676-1683. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2016.11.23. eCollection 2016. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27990375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal keratitis: study of increasing trend and common determinants.Nepal J Epidemiol. 2017 Jun 30;7(2):685-693. doi: 10.3126/nje.v7i2.17975. eCollection 2017 Jun. Nepal J Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 29181230 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the IL-33/ST2/p38 signaling pathway in the immune response of corneal epithelial cells to Aspergillus fumigatus infection.Int J Ophthalmol. 2019 Apr 18;12(4):549-556. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2019.04.04. eCollection 2019. Int J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31024805 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

