A Combined Pharmacophore Modeling, 3D QSAR and Virtual Screening Studies on Imidazopyridines as B-Raf Inhibitors
- PMID: 26035757
- PMCID: PMC4490445
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160612307
A Combined Pharmacophore Modeling, 3D QSAR and Virtual Screening Studies on Imidazopyridines as B-Raf Inhibitors
Abstract
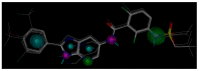
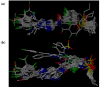
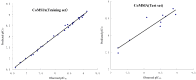
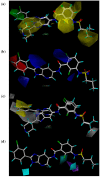
B-Raf kinase is an important target in treatment of cancers. In order to design and find potent B-Raf inhibitors (BRIs), 3D pharmacophore models were created using the Genetic Algorithm with Linear Assignment of Hypermolecular Alignment of Database (GALAHAD). The best pharmacophore model obtained which was used in effective alignment of the data set contains two acceptor atoms, three donor atoms and three hydrophobes. In succession, comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) were performed on 39 imidazopyridine BRIs to build three dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D QSAR) models based on both pharmacophore and docking alignments. The CoMSIA model based on the pharmacophore alignment shows the best result (q(2) = 0.621, r(2)(pred) = 0.885). This 3D QSAR approach provides significant insights that are useful for designing potent BRIs. In addition, the obtained best pharmacophore model was used for virtual screening against the NCI2000 database. The hit compounds were further filtered with molecular docking, and their biological activities were predicted using the CoMSIA model, and three potential BRIs with new skeletons were obtained.
Keywords: 3D QSAR; B-Raf inhibitors; imidazopyridine; pharmacophore; virtual screening.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3D QSAR studies, pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening on a series of steroidal aromatase inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Nov 14;15(11):20927-47. doi: 10.3390/ijms151120927. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25405729 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual screening of B-Raf kinase inhibitors: A combination of pharmacophore modelling, molecular docking, 3D-QSAR model and binding free energy calculation studies.Comput Biol Chem. 2017 Oct;70:186-190. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2017.08.017. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Comput Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28892749
-
Analysis of B-Raf[Formula: see text] inhibitors using 2D and 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and pharmacophore studies.Mol Divers. 2015 Nov;19(4):915-30. doi: 10.1007/s11030-015-9626-y. Epub 2015 Aug 15. Mol Divers. 2015. PMID: 26276566
-
Innovative computer-aided methods for the discovery of new kinase ligands.Future Med Chem. 2016 Apr;8(5):509-26. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2015-0003. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Future Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27105126 Review.
-
Receptor-based 3D-QSAR in Drug Design: Methods and Applications in Kinase Studies.Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(13):1463-77. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150915120943. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26369822 Review.
Cited by
-
An Investigation of Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulation on Imidazopyridines as B-Raf Kinase Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 16;16(11):27350-61. doi: 10.3390/ijms161126026. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26580609 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-Aided Drug Design Boosts RAS Inhibitor Discovery.Molecules. 2022 Sep 5;27(17):5710. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175710. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential ACAT-2 selective inhibitors using pharmacophore, SVM and SVR from Chinese herbs.Mol Divers. 2016 Nov;20(4):933-944. doi: 10.1007/s11030-016-9684-9. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Mol Divers. 2016. PMID: 27329301
-
Combined Minimum-Run Resolution IV and Central Composite Design for Optimized Removal of the Tetracycline Drug Over Metal⁻Organic Framework-Templated Porous Carbon.Molecules. 2019 May 16;24(10):1887. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101887. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31100932 Free PMC article.
-
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) as a Potential Target for Anticancer Drug Design and Development.Molecules. 2021 Oct 4;26(19):6019. doi: 10.3390/molecules26196019. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El-Azab A.S., Al-Omar M.A., Abdel-Aziz A.M., Abdel-Aziz N.I., El-Sayed A.A., Aleisa A.M., Sayed-Ahmed M.M., Abdel-Hamide S.G. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel quinazoline derivatives as potential antitumor agents: Molecular docking study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010;45:4188–4198. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.06.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li N., Batt D., Warmuth M. B-Raf kinase inhibitors for cancer treatment. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2007;8:452–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

