The Importance of IL-6 in the Development of LAT-Mediated Autoimmunity
- PMID: 26034173
- PMCID: PMC4491041
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403187
The Importance of IL-6 in the Development of LAT-Mediated Autoimmunity
Abstract
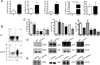
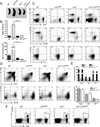
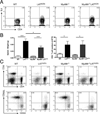
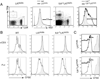
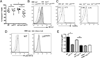
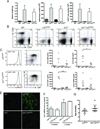
Linker for activation of T cells (LAT) is a transmembrane adaptor protein that is highly tyrosine phosphorylated upon engagement of the TCR. Phosphorylated LAT binds Grb2, Gads, and phospholipase C (PLC)γ1 to mediate T cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. T cells from mice harboring a mutation at the PLCγ1 binding site of LAT (Y136F) have impaired calcium flux and Erk activation. Interestingly, these T cells are highly activated, resulting in the development of a lymphoproliferative syndrome in these mice. CD4(+) T cells in LATY136F mice are Th2 skewed, producing large amounts of IL-4. In this study, we showed that the LATY136F T cells could also overproduce IL-6 due to activated NF-κB, AKT, and p38 pathways. By crossing LATY136F mice with IL-6-deficient mice, we demonstrated that IL-6 is required for uncontrolled T cell expansion during the early stage of disease development. Reduced CD4(+) T cell expansion was not due to a further block in thymocyte development or an increase in the number of regulatory T cells, but was caused by reduction in cell survival. In aged IL-6(-/-) LATY136F mice, CD4(+) T cells began to hyperproliferate and induced splenomegaly; however, isotype switching and autoantibody production were diminished. Our data indicated that the LAT-PLCγ1 interaction is important for controlling IL-6 production by T cells and demonstrated a critical role of IL-6 in the development of this lymphoproliferative syndrome.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of LAT-PLCγ1 interaction in γδ T cell development and homeostasis.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 15;192(6):2865-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302493. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24523509 Free PMC article.
-
LAT-mediated signaling in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell development.J Exp Med. 2006 Jan 23;203(1):119-29. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050903. Epub 2005 Dec 27. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16380508 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of LAT in the activation, homeostasis, and regulatory function of T cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 12;285(46):35393-405. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.145052. Epub 2010 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20837489 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the LAT adaptor in T-cell development and Th2 differentiation.Adv Immunol. 2005;87:1-25. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(05)87001-4. Adv Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16102570 Review.
-
Activation of T lymphocytes and the role of the adapter LAT.Transpl Immunol. 2006 Dec;17(1):23-6. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2006.09.013. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Transpl Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17157209 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of the key genes and long non‑coding RNAs in ankylosing spondylitis using RNA sequencing.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Mar;43(3):1179-1192. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.4038. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30592273 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontitis Impact in Interleukin-6 Serum Levels in Solid Organ Transplanted Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Mar 27;10(4):184. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10040184. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32230707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimal timing of steroid initiation in response to CTLA-4 antibody in metastatic cancer: A mathematical model.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 10;17(11):e0277248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277248. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36355837 Free PMC article.
-
Direct On-Chip Differentiation of Intestinal Tubules from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 14;21(14):4964. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144964. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32674311 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-associated lymphopenia: possible mechanisms and the role of CD147.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 4;22(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01718-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38965547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hirano T, Nakajima K, Hibi M. Signaling mechanisms through gp130: a model of the cytokine system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997;8:241–252. - PubMed
-
- Naugler WE, Karin M. The wolf in sheep's clothing: the role of interleukin-6 in immunity, inflammation and cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14:109–119. - PubMed
-
- Wegiel B, Bjartell A, Culig Z, Persson JL. Interleukin-6 activates PI3K/Akt pathway and regulates cyclin A1 to promote prostate cancer cell survival. Int J Cancer. 2008;122:1521–1529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

