Error-Prone Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks
- PMID: 26033759
- PMCID: PMC4586358
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25053
Error-Prone Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks
Abstract
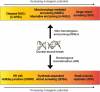
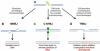
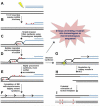
Preserving the integrity of the DNA double helix is crucial for the maintenance of genomic stability. Therefore, DNA double-strand breaks represent a serious threat to cells. In this review, we describe the two major strategies used to repair double strand breaks: non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination, emphasizing the mutagenic aspects of each. We focus on emerging evidence that homologous recombination, long thought to be an error-free repair process, can in fact be highly mutagenic, particularly in contexts requiring large amounts of DNA synthesis. Recent investigations have begun to illuminate the molecular mechanisms by which error-prone double-strand break repair can create major genomic changes, such as translocations and complex chromosome rearrangements. We highlight these studies and discuss proposed models that may explain some of the more extreme genetic changes observed in human cancers and congenital disorders.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[The main repair pathways of double-strand breaks in the genomic DNA and interactions between them].Tsitol Genet. 2014 May-Jun;48(3):64-77. Tsitol Genet. 2014. PMID: 25019146 Review. Russian.
-
Double-strand break repair and homologous recombination in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Yeast. 2006 Oct 15;23(13):963-76. doi: 10.1002/yea.1414. Yeast. 2006. PMID: 17072889 Review.
-
Genomic rearrangements induced by unscheduled DNA double strand breaks in somatic mammalian cells.FEBS J. 2017 Aug;284(15):2324-2344. doi: 10.1111/febs.14053. Epub 2017 Mar 22. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28244221 Review.
-
Collaboration and competition between DNA double-strand break repair pathways.FEBS Lett. 2010 Sep 10;584(17):3703-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.07.057. Epub 2010 Aug 5. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20691183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coping with DNA double strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1256-63. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.018. Epub 2010 Nov 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 21115283 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers beyond BRCA: promising combinatorial treatment strategies in overcoming resistance to PARP inhibitors.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Oct 25;29(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00870-7. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36284291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Gene Therapeutics for Epidermolysis Bullosa under Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 13;25(4):2243. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042243. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic investigation of BRCA1-A, -B, and -C complexes and their functions in DNA damage response and DNA repair.Oncogene. 2024 Aug;43(35):2621-2634. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03108-y. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39068216
-
Role of PRMT1 and PRMT5 in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 14;25(16):8854. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168854. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-efficiency nonhomologous insertion of a foreign gene into the herpes simplex virus genome.J Gen Virol. 2020 Sep;101(9):982-996. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001451. J Gen Virol. 2020. PMID: 32602833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boboila C, Alt FW, Schwer B. Classical and alternative end-joining pathways for repair of lymphocyte-specific and general DNA double-strand breaks. Adv Immunol. 2012;116:1–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

