TXA709, an FtsZ-Targeting Benzamide Prodrug with Improved Pharmacokinetics and Enhanced In Vivo Efficacy against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 26033735
- PMCID: PMC4505295
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00708-15
TXA709, an FtsZ-Targeting Benzamide Prodrug with Improved Pharmacokinetics and Enhanced In Vivo Efficacy against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
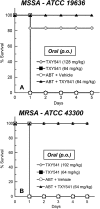
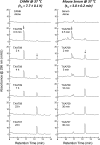
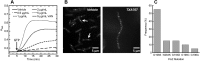
The clinical development of FtsZ-targeting benzamide compounds like PC190723 has been limited by poor drug-like and pharmacokinetic properties. Development of prodrugs of PC190723 (e.g., TXY541) resulted in enhanced pharmaceutical properties, which, in turn, led to improved intravenous efficacy as well as the first demonstration of oral efficacy in vivo against both methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Despite being efficacious in vivo, TXY541 still suffered from suboptimal pharmacokinetics and the requirement of high efficacious doses. We describe here the design of a new prodrug (TXA709) in which the Cl group on the pyridyl ring has been replaced with a CF3 functionality that is resistant to metabolic attack. As a result of this enhanced metabolic stability, the product of the TXA709 prodrug (TXA707) is associated with improved pharmacokinetic properties (a 6.5-fold-longer half-life and a 3-fold-greater oral bioavailability) and superior in vivo antistaphylococcal efficacy relative to PC190723. We validate FtsZ as the antibacterial target of TXA707 and demonstrate that the compound retains potent bactericidal activity against S. aureus strains resistant to the current standard-of-care drugs vancomycin, daptomycin, and linezolid. These collective properties, coupled with minimal observed toxicity to mammalian cells, establish the prodrug TXA709 as an antistaphylococcal agent worthy of clinical development.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
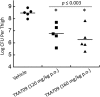
Similar articles
-
Combining the FtsZ-Targeting Prodrug TXA709 and the Cephalosporin Cefdinir Confers Synergy and Reduces the Frequency of Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jun 20;60(7):4290-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00613-16. Print 2016 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27161635 Free PMC article.
-
An FtsZ-targeting prodrug with oral antistaphylococcal efficacy in vivo.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Dec;57(12):5860-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01016-13. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 24041882 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Antibacterial Characterization of a New Benzamide FtsZ Inhibitor with Superior Bactericidal Activity and In Vivo Efficacy Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 Mar 17;18(3):629-642. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00934. Epub 2023 Feb 28. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 36854145 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative agents to vancomycin for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections.Am J Ther. 2013 Mar-Apr;20(2):200-12. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e31821109ec. Am J Ther. 2013. PMID: 21642833 Review.
-
FtsZ inhibitors as a new genera of antibacterial agents.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Oct;91:103169. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103169. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31398602 Review.
Cited by
-
Combining the FtsZ-Targeting Prodrug TXA709 and the Cephalosporin Cefdinir Confers Synergy and Reduces the Frequency of Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jun 20;60(7):4290-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00613-16. Print 2016 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27161635 Free PMC article.
-
Mycopyranone: a 8,8'-binaphthopyranone with potent anti-MRSA activity from the fungus Phialemoniopsis sp.Tetrahedron Lett. 2019 Feb 21;60(8):594-597. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.01.029. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019. PMID: 31598014 Free PMC article.
-
β-Lactam Antibiotics with a High Affinity for PBP2 Act Synergistically with the FtsZ-Targeting Agent TXA707 against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Aug 24;61(9):e00863-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00863-17. Print 2017 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28630190 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical Approaches on Antimicrobial Resistance: Prospects and Challenges.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Aug 14;10(8):981. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080981. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient Synthesis of Amine-Linked 2,4,6-Trisubstituted Pyrimidines as a New Class of Bacterial FtsZ Inhibitors.ACS Omega. 2017 Oct 31;2(10):7281-7292. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b00701. Epub 2017 Oct 27. ACS Omega. 2017. PMID: 30023544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. September 2013. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2013. CDC, Atlanta, GA: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/.
-
- Hanaki H, Cui L, Ikeda-Dantsuji Y, Nakae T, Honda J, Yanagihara K, Takesue Y, Matsumoto T, Sunakawa K, Kaku M, Tomono K, Fukuchi K, Kusachi S, Mikamo H, Takata T, Otsuka Y, Nagura O, Fujitani S, Aoki Y, Yamaguchi Y, Tateda K, Kadota J, Kohno S, Niki Y. 2014. Antibiotic susceptibility survey of blood-borne MRSA isolates in Japan from 2008 through 2011. J Infect Chemother 20:527–534. doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2014.06.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

