Inhibition of cell adhesion and immune responses in the mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis with a peptidomimetic that blocks CD2-CD58 interface interactions
- PMID: 26031942
- PMCID: PMC4666829
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.22692
Inhibition of cell adhesion and immune responses in the mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis with a peptidomimetic that blocks CD2-CD58 interface interactions
Abstract
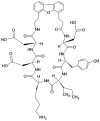
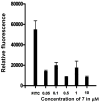
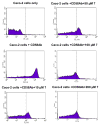
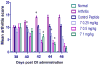
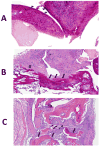
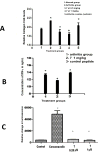
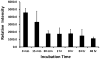
CD2 and CD58 are two important costimulatory molecules involved in generating the signal II required for normal immune signaling. However, this interaction can be targeted to be of benefit in cases of abnormal immune signaling seen in autoimmune diseases. Our objective in this study was to design a peptidomimetic (compound 7) based on a β-strand structure of the adhesion domain of CD2 protein to inhibit CD2-CD58 protein-protein interaction and its effect on immunomodulation in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model. The ability of compound 7 to bind to CD58 protein was assessed using flow cytometry. The effect of compound 7 on modulating the immune response was evaluated in an autoimmune disease using CIA in mice. The stability of compound 7 was evaluated in mouse serum using mass spectrometry. Antibody (Ab) binding inhibition studies suggested that compound 7 binds to CD58 protein. Compound 7 was successful in modulating immune responses when administered in the CIA mouse model along with reducing anti-collagen Ab levels and decreasing the level of interferon gamma (IFN-γ) relative to control treatments. Compound 7 was found to be nonimmunogenic and stable in mouse serum up to 48 h. Results suggest that compound 7 can serve as a lead compound for immunomodulation, and could be a therapeutic agent for the autoimmune disease rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Keywords: costimulatory molecules; immunomodulation; peptidomimetic; protein−protein interaction; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
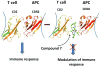
Similar articles
-
Targeting protein-protein interaction for immunomodulation: A sunflower trypsin inhibitor analog peptidomimetic suppresses RA progression in CIA model.J Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Jul;149(3):124-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2022.04.005. Epub 2022 Apr 25. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35641025 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppression by co-stimulatory molecules: inhibition of CD2-CD48/CD58 interaction by peptides from CD2 to suppress progression of collagen-induced arthritis in mice.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2013 Jul;82(1):106-18. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12138. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2013. PMID: 23530775 Free PMC article.
-
A peptide from the beta-strand region of CD2 protein that inhibits cell adhesion and suppresses arthritis in a mouse model.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2010 Sep 1;76(3):234-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2010.01001.x. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2010. PMID: 20572813 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotypic cell adhesion assay for the study of cell adhesion inhibition.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;716:225-43. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-012-6_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21318910
-
A novel, rapid and sensitive heterotypic cell adhesion assay for CD2-CD58 interaction, and its application for testing inhibitory peptides.J Immunol Methods. 2004 Aug;291(1-2):39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2004.04.026. J Immunol Methods. 2004. PMID: 15345303
Cited by
-
Structure-based identification of inhibitors disrupting the CD2-CD58 interactions.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021 Mar;35(3):337-353. doi: 10.1007/s10822-020-00369-z. Epub 2021 Feb 3. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021. PMID: 33532888
-
Roles of CD48 in regulating immunity and tolerance.Clin Immunol. 2016 Mar;164:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26794910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD58 Immunobiology at a Glance.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 8;12:705260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.705260. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34168659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic profiling of extracellular vesicles in synovial fluid and plasma from Oligoarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis patients reveals novel immunopathogenic biomarkers.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 27;14:1134747. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1134747. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37205098 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of co-stimulatory signal from CD2-CD58 proteins by a grafted peptide.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Mar;97(3):607-627. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13797. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 32946175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Merwe PA, Davis SJ. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:659–684. - PubMed
-
- Hutchings NJ, Clarkson N, Chalkley R, Barclay AN, Brown MH. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:22396–22403. - PubMed
-
- Kanner SB, Damle NK, Blake J, Aruffo A, Ledbetter JA. J Immunol. 1992;148:2023–2029. - PubMed
-
- Martelli MP, Lin H, Zhang W, Samelson LE, Bierer BE. Blood. 2000;96:2181–2190. - PubMed
-
- Espagnolle N, Depoil D, Zaru R, Demeur C, Champagne E, Guiraud M, Valitutti S. Int Immunol. 2007;19:239–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

