IRE1α-Dependent Decay of CReP/Ppp1r15b mRNA Increases Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2α Phosphorylation and Suppresses Protein Synthesis
- PMID: 26031337
- PMCID: PMC4508316
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00215-15
IRE1α-Dependent Decay of CReP/Ppp1r15b mRNA Increases Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2α Phosphorylation and Suppresses Protein Synthesis
Abstract
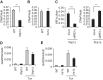
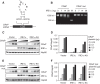
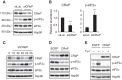
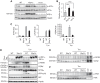
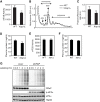
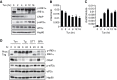
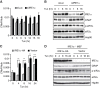
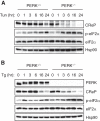
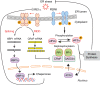
The unfolded protein response (UPR) regulates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis and protects cells from ER stress. IRE1α is a central regulator of the UPR that activates the transcription factor XBP1s through an unconventional splicing mechanism using its endoribonuclease activity. IRE1α also cleaves certain mRNAs containing XBP1-like secondary structures to promote the degradation of these mRNAs, a process known as regulated IRE1α-dependent decay (RIDD). We show here that the mRNA of CReP/Ppp1r15b, a regulatory subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α) phosphatase, is a RIDD substrate. eIF2α plays a central role in the integrated stress response by mediating the translational attenuation to decrease the stress level in the cell. CReP expression was markedly suppressed in XBP1-deficient mice livers due to hyperactivated IRE1α. Decreased CReP expression caused the induction of eIF2α phosphorylation and the attenuation of protein synthesis in XBP1-deficient livers. ER stress also suppressed CReP expression in an IRE1α-dependent manner, which increased eIF2α phosphorylation and consequently attenuated protein synthesis. Taken together, the results of our study reveal a novel function of IRE1α in the regulation of eIF2α phosphorylation and the translational control.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The PPP1R15 Family of eIF2-alpha Phosphatase Targeting Subunits (GADD34 and CReP).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 10;24(24):17321. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417321. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel feedback loop regulates the response to endoplasmic reticulum stress via the cooperation of cytoplasmic splicing and mRNA translation.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Mar;32(5):992-1003. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06665-11. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22215619 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage of BLOC1S1 mRNA by IRE1 Is Sequence Specific, Temporally Separate from XBP1 Splicing, and Dispensable for Cell Viability under Acute Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jun;35(12):2186-202. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00013-15. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25870107 Free PMC article.
-
The unfolded protein response sensor IRE1alpha is required at 2 distinct steps in B cell lymphopoiesis.J Clin Invest. 2005 Feb;115(2):268-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI21848. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15690081 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple roles of the unfolded protein response regulator IRE1α in cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Sep;58(9):1623-1630. doi: 10.1002/mc.23031. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 31041814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The PPP1R15 Family of eIF2-alpha Phosphatase Targeting Subunits (GADD34 and CReP).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 10;24(24):17321. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417321. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Immune Responses.Mol Cells. 2018 Aug 31;41(8):705-716. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.0241. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Mol Cells. 2018. PMID: 30078231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5,7,3',4'-Tetramethoxyflavone protects chondrocytes from ER stress-induced apoptosis through regulation of the IRE1α pathway.Connect Tissue Res. 2018 Mar;59(2):157-166. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2017.1321639. Epub 2017 May 23. Connect Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 28436754 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated IRE1-dependent mRNA decay sets the threshold for dendritic cell survival.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;19(6):698-710. doi: 10.1038/ncb3518. Epub 2017 May 1. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28459443 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated rht-PA Processing in CHO Cells: Influence of Mild Hypothermia and Specific Growth Rates in Batch and Chemostat Cultures.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0144224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144224. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26659083 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
