Twist1 and Twist2 Contribute to Cytokine Downregulation following Chronic NOD2 Stimulation of Human Macrophages through the Coordinated Regulation of Transcriptional Repressors and Activators
- PMID: 26019273
- PMCID: PMC4501480
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402808
Twist1 and Twist2 Contribute to Cytokine Downregulation following Chronic NOD2 Stimulation of Human Macrophages through the Coordinated Regulation of Transcriptional Repressors and Activators
Abstract
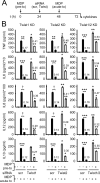
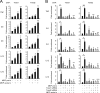
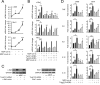
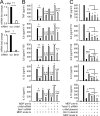
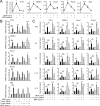
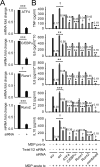
Proper regulation of microbial-induced cytokines is critical to intestinal immune homeostasis. Acute stimulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2 (NOD2), the Crohn's disease-associated sensor of bacterial peptidoglycan, induces cytokines. However, chronic NOD2 stimulation in macrophages decreases cytokines upon pattern recognition receptor (PRR) restimulation; cytokine attenuation to PRR stimulation is similarly observed in intestinal macrophages. The role for the transcriptional repressors Twist1 and Twist2 in regulating PRR-induced cytokine outcomes is poorly understood and has not been reported for NOD2. We found that Twist1 and Twist2 were required for optimal cytokine downregulation during acute and, particularly, chronic NOD2 stimulation of human macrophages. Consistently, Twist1 and Twist2 expression was increased after chronic NOD2 stimulation; this increased expression was IL-10 and TGF-β dependent. Although Twist1 and Twist2 did not coregulate each other's expression, they cooperated to enhance binding to cytokine promoters after chronic NOD2 stimulation. Moreover, Twist1 and Twist2 contributed to enhance expression and promoter binding of the proinflammatory inhibitor c-Maf and the transcriptional repressor Bmi1. Restoring c-Maf and Bmi1 expression in Twist-deficient macrophages restored NOD2-induced cytokine downregulation. Furthermore, with chronic NOD2 stimulation, Twist1 and Twist2 contributed to the decreased expression and cytokine promoter binding of the transcriptional activators activating transcription factor 4, C/EBPα, Runx1, and Runx2. Knockdown of these transcriptional activators in Twist-deficient macrophages restored cytokine downregulation after chronic NOD2 stimulation. Finally, NOD2 synergized with additional PRRs to increase Twist1 and Twist2 expression and Twist-dependent pathways. Therefore, after chronic NOD2 stimulation Twist1 and Twist2 coordinate the regulation of both transcriptional activators and repressors, thereby mediating optimal cytokine downregulation.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
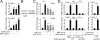
Similar articles
-
Twist1 and Twist2 Induce Human Macrophage Memory upon Chronic Innate Receptor Treatment by HDAC-Mediated Deacetylation of Cytokine Promoters.J Immunol. 2019 Jun 1;202(11):3297-3308. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800757. Epub 2019 Apr 26. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31028123 Free PMC article.
-
TAM receptor-dependent regulation of SOCS3 and MAPKs contributes to proinflammatory cytokine downregulation following chronic NOD2 stimulation of human macrophages.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 15;194(4):1928-37. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401933. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25567680 Free PMC article.
-
LPS induces the degradation of programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) to release Twist2, activating c-Maf transcription to promote interleukin-10 production.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 15;289(33):22980-22990. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.573089. Epub 2014 Jun 30. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24982420 Free PMC article.
-
Redundant or separate entities?--roles of Twist1 and Twist2 as molecular switches during gene transcription.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Mar;39(4):1177-86. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq890. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20935057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological function and molecular mechanism of Twist2.Yi Chuan. 2015 Jan;37(1):17-24. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.2015.01.003. Yi Chuan. 2015. PMID: 25608809 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) E2 Repression of TWIST1 Transcription Is a Potential Mediator of HPV16 Cancer Outcomes.mSphere. 2020 Dec 9;5(6):e00981-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00981-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 33298572 Free PMC article.
-
BACH2 regulates diversification of regulatory and proinflammatory chromatin states in TH17 cells.Nat Immunol. 2024 Aug;25(8):1395-1410. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01901-1. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39009838
-
Twist1: A Double-Edged Sword in Kidney Diseases.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020 Jul;6(4):247-257. doi: 10.1159/000505188. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32903940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcription factor Twist1 in the distal nephron but not in macrophages propagates aristolochic acid nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2020 Jan;97(1):119-129. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.07.016. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 31685313 Free PMC article.
-
Twist1 in podocytes ameliorates podocyte injury and proteinuria by limiting CCL2-dependent macrophage infiltration.JCI Insight. 2021 Aug 9;6(15):e148109. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.148109. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34369383 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

