The Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitor BIX01294 Inhibits HIF-1α Stability and Angiogenesis
- PMID: 26013382
- PMCID: PMC4469910
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2015.0026
The Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitor BIX01294 Inhibits HIF-1α Stability and Angiogenesis
Abstract
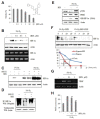
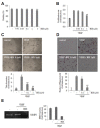
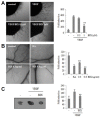
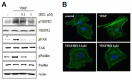
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is a key regulator of tumor growth and angiogenesis. Recent studies have shown that, BIX01294, a G9a histone methyltransferase (HMT)-specific inhibitor, induces apoptosis and inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of cancer cells. However, not many studies have investigated whether inhibition of G9a HMT can modulate HIF-1α stability and angiogenesis. Here, we show that BIX01294 dose-dependently decreases levels of HIF-1α in HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. The half-life of HIF-1α, expression of proline hydroxylase 2 (PHD2), hydroxylated HIF-1α and von Hippel-Lindau protein (pVHL) under hypoxic conditions were decreased by BIX01294. The mRNA expression and secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were also significantly reduced by BIX01294 under hypoxic conditions in HepG2 cells. BIX01294 remarkably decreased angiogenic activity induced by VEGF in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo, as demonstrated by assays using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), mouse aortic rings, and chick chorioallantoic membranes (CAMs), respectively. Furthermore, BIX01294 suppressed VEGF-induced matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) activity and inhibited VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR-2), focal adhesion kinase (FAK), and paxillin in HUVECs. In addition, BIX01294 inhibited VEGF-induced formation of actin cytoskeletal stress fibers. In conclusion, we demonstrated that BIX01294 inhibits HIF-1α stability and VEGF-induced angiogenesis through the VEGFR-2 signaling pathway and actin cytoskeletal remodeling, indicating a promising approach for developing novel therapeutics to stop tumor progression.
Keywords: BIX01294; G9a HMT inhibitor; HIF-1α; angiogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Abedi H, Zachary I. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation and recruitment to new focal adhesions of focal adhesion kinase and paxillin in endothelial cells. J. Bio. Chem. 1997;272:15442–15451. - PubMed
-
- Bardos JI, Ashcroft J. Negative and positive regulation of HIF-1: a complex network. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2005;1755:107–120. - PubMed
-
- Carroll VA, Ashcroft M. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α versus HIF-2α in the regulation of HIF target genes in response to hypoxia, insulin-like growth factor-I, or loss of von hippel-lindau function: implications for targeting the HIF pathway. Cancer Res. 2008;15:6264–6270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

