Health-related quality of life in patients with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis in the era of biologics: data from the German biologics register RABBIT
- PMID: 26001633
- PMCID: PMC4571489
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev194
Health-related quality of life in patients with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis in the era of biologics: data from the German biologics register RABBIT
Abstract
Objective: To compare the 24-month course of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with long-standing RA treated with a conventional synthetic (cs) or a first, second or third biologic (b) DMARD in daily rheumatological care.
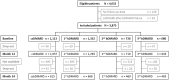
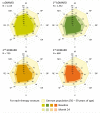
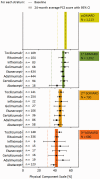
Methods: Patients enrolled in the German biologics register RABBIT who were observed over at least 12 months were stratified according to the nth bDMARD started at enrolment. HRQoL was captured by the SF36 health survey. Within strata of sequential bDMARD therapy, we examined patients' HRQoL at baseline and at follow-ups in comparison with the general population, the 24-month course of HRQoL of different bDMARDs and the proportion of patients exceeding the minimal detectable improvement of physical and mental health sum scores.
Results: All patients reported remarkably lower scores of physical and mental health than the general population at baseline and month 12. In each stratum of sequential bDMARD therapy, patients improved significantly by month 12 and remained stable until month 24. The improvement of HRQoL was not attributable to a particular bDMARD. The following proportions of patients exceeded the minimal detectable improvement of at least 17.85 Physical Component Scale scores or 22.18 Mental Component Scale score points: csDMARD (n = 1113) 31.1%/22.3%, first bDMARD (n = 1352) 39.9%/29.7%, second bDMARD (n = 730) 37.3%/26.2% and third bDMARD (n = 680) 34.2%/30.9%.
Conclusion: Lasting improvement of both physical and mental health is achievable even for severely affected RA patients with a history of more than one bDMARD failure. Nevertheless, impairment of HRQoL in RA patients is enormous compared with the general population.
Keywords: biologics register; health-related quality of life; minimal detectable change; rheumatoid arthritis.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Characteristics and Cytokine Profiles of Organizing Pneumonia in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with or without Biologics.J Rheumatol. 2016 Apr;43(4):738-44. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.151019. Epub 2016 Feb 1. J Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26834212
-
Effectiveness and drug adherence of biologic monotherapy in routine care of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cohort study of patients registered in the Danish biologics registry.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Dec;54(12):2156-65. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev216. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 26175471
-
Biologic refractory disease in rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Oct;77(10):1405-1412. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213378. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 29980575 Free PMC article.
-
Monotherapy with biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017 May 1;56(5):689-697. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew271. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017. PMID: 27550301 Review.
-
[Characteristics of pharmacotherapy in older patients with rheumatism].Z Rheumatol. 2018 Jun;77(5):369-378. doi: 10.1007/s00393-018-0460-3. Z Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29691687 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Quality of life, sleep and rheumatoid arthritis (QUASAR): a protocol for a prospective UK mHealth study to investigate the relationship between sleep and quality of life in adults with rheumatoid arthritis.BMJ Open. 2018 Jan 26;8(1):e018752. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018752. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29374666 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep problems in rheumatoid arthritis over 12 years from diagnosis: results from the Swedish EIRA study.RMD Open. 2022 Jan;8(1):e001800. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001800. RMD Open. 2022. PMID: 34987091 Free PMC article.
-
Economic and Humanistic Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results From the US National Survey Data 2018-2020.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024 Nov;6(11):746-754. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11728. Epub 2024 Aug 6. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39105293 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that affect the assessment of the quality of life of rheumatoid arthritis patients depending on the prevalence of frailty syndrome.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020 Jul 6;18(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01472-3. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 32631349 Free PMC article.
-
[Latest findings from the RABBIT register].Z Rheumatol. 2022 Mar;81(2):100-109. doi: 10.1007/s00393-021-01139-4. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Z Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 34940891 Free PMC article. Review. German.
References
-
- Gabriel SE. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2001;27:269–81. - PubMed
-
- Lee DM, Weinblatt ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2001;358:903–11. - PubMed
-
- Husted JA, Gladman DD, Farewell VT, Cook RJ. Health-related quality of life of patients with psoriatic arthritis: a comparison with patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2001;45:151–8. - PubMed
-
- Kosinski M, Kujawski SC, Martin R, et al. Health-related quality of life in early rheumatoid arthritis: impact of disease and treatment response. Am J Manag Care 2002;8:231–40. - PubMed
-
- Uhlig T, Loge JH, Kristiansen IS, Kvien TK. Quantification of reduced health-related quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to the general population. J Rheumatol 2007;34:1241–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

