The cancer cell map initiative: defining the hallmark networks of cancer
- PMID: 26000852
- PMCID: PMC5359018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.05.008
The cancer cell map initiative: defining the hallmark networks of cancer
Abstract
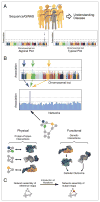
Progress in DNA sequencing has revealed the startling complexity of cancer genomes, which typically carry thousands of somatic mutations. However, it remains unclear which are the key driver mutations or dependencies in a given cancer and how these influence pathogenesis and response to therapy. Although tumors of similar types and clinical outcomes can have patterns of mutations that are strikingly different, it is becoming apparent that these mutations recurrently hijack the same hallmark molecular pathways and networks. For this reason, it is likely that successful interpretation of cancer genomes will require comprehensive knowledge of the molecular networks under selective pressure in oncogenesis. Here we announce the creation of a new effort, The Cancer Cell Map Initiative (CCMI), aimed at systematically detailing these complex interactions among cancer genes and how they differ between diseased and healthy states. We discuss recent progress that enables creation of these cancer cell maps across a range of tumor types and how they can be used to target networks disrupted in individual patients, significantly accelerating the development of precision medicine.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mapping the protein-protein and genetic interactions of cancer to guide precision medicine.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2019 Feb;54:110-117. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2019. PMID: 31288129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive genomics: a cancer hallmark network framework for predicting tumor clinical phenotypes using genome sequencing data.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Feb;30:4-12. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 24747696 Review.
-
Pathway-based dissection of the genomic heterogeneity of cancer hallmarks' acquisition with SLAPenrich.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 30;8(1):6713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25076-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29713020 Free PMC article.
-
RDF SKETCH MAPS - KNOWLEDGE COMPLEXITY REDUCTION FOR PRECISION MEDICINE ANALYTICS.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2016;21:417-28. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2016. PMID: 26776205
-
Typing tumors using pathways selected by somatic evolution.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 8;9(1):4159. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06464-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30297789 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The extracellular matrix as a key regulator of intracellular signalling networks.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;176(1):82-92. doi: 10.1111/bph.14195. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29510460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Perspective on Implementing a Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Platform for Drug Discovery and the Advancement of Personalized Medicine.J Biomol Screen. 2016 Jul;21(6):521-34. doi: 10.1177/1087057116635818. Epub 2016 Mar 8. J Biomol Screen. 2016. PMID: 26962875 Free PMC article.
-
Unbiased Identification of Blood-based Biomarkers for Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Modeling and Mining Molecular Interaction Networks.EBioMedicine. 2017 Feb;15:112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.12.009. Epub 2016 Dec 21. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 28065665 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial CRISPR-Cas9 screens for de novo mapping of genetic interactions.Nat Methods. 2017 Jun;14(6):573-576. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4225. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Nat Methods. 2017. PMID: 28319113 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Profiling of Kinase Dependencies in Cancer Cell Lines.Cell Rep. 2016 Mar 15;14(10):2490-501. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.023. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26947069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amabile G, Meissner A. Induced pluripotent stem cells: current progress and potential for regenerative medicine. Trends in molecular medicine. 2009;15:59–68. - PubMed
-
- Amundadottir L, Kraft P, Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Fuchs CS, Petersen GM, Arslan AA, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Gross M, Helzlsouer K, Jacobs EJ. Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the ABO locus associated with susceptibility to pancreatic cancer. Nature genetics. 2009;41:986–990. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashworth A, Lord CJ, Reis-Filho JS. Genetic interactions in cancer progression and treatment. Cell. 2011;145:30–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

