Inhibition of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 enhances TLR-mediated inflammation and promotes endotoxin-driven organ failure
- PMID: 25993992
- PMCID: PMC4550376
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.15-270462
Inhibition of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 enhances TLR-mediated inflammation and promotes endotoxin-driven organ failure
Abstract
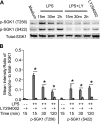
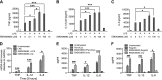
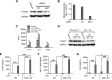
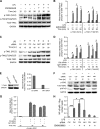
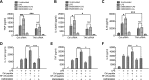
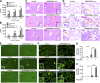
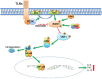
Serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase (SGK)1 is associated with several important pathologic conditions and plays a modulatory role in adaptive immune responses. However, the involvement and functional role of SGK1 in innate immune responses remain entirely unknown. In this study, we establish that SGK1 is a novel and potent negative regulator of TLR-induced inflammation. Pharmacologic inhibition of SGK1 or suppression by small interfering RNA enhances proinflammatory cytokine (TNF, IL-12, and IL-6) production in TLR-engaged monocytes, a result confirmed in Cre-loxP-mediated SGK1-deficient cells. SGK1 inhibition or gene deficiency results in increased phosphorylation of IKK, IκBα, and NF-κB p65 in LPS-stimulated cells. Enhanced NF-κB p65 DNA binding also occurs upon SGK1 inhibition. The subsequent enhancement of proinflammatory cytokines is dependent on the phosphorylation of TGF-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), as confirmed by TAK1 gene silencing. In vivo relevance was established in a murine endotoxin model, in which we found that SGK1 inhibition aggravates the severity of multiple organ damage and enhances the inflammatory response by heightening both proinflammatory cytokine levels and neutrophil infiltration. These findings have identified an anti-inflammatory function of SGK1, elucidated the underlying intracellular mechanisms, and establish, for the first time, that SGK1 holds potential as a novel target for intervention in the control of inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: LPS; SGK1; TAK1; inflammatory cytokines.
© FASEB.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SGK1 negatively regulates inflammatory immune responses and protects against alveolar bone loss through modulation of TRAF3 activity.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;298(6):102036. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102036. Epub 2022 May 17. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35588785 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal role of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 in vascular inflammation and atherogenesis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Mar;35(3):547-57. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304454. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25614279
-
The role of JAK-3 in regulating TLR-mediated inflammatory cytokine production in innate immune cells.J Immunol. 2013 Aug 1;191(3):1164-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203084. Epub 2013 Jun 24. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23797672 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinase inhibition.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013 Jun;22(6):701-14. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2013.778971. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23506284 Review.
-
Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) as an emerging therapeutic target for cardiac diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Oct;208:107369. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107369. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 39209082 Review.
Cited by
-
AGC kinase inhibitors regulate STING signaling through SGK-dependent and SGK-independent mechanisms.Cell Chem Biol. 2023 Dec 21;30(12):1601-1616.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Cell Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37939709 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper: A Novel Anti-inflammatory Molecule.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 27;10:308. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00308. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30971930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGK1 negatively regulates inflammatory immune responses and protects against alveolar bone loss through modulation of TRAF3 activity.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;298(6):102036. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102036. Epub 2022 May 17. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35588785 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced phosphorylation by CDK9 modulates the coactivator functions of transcriptional cofactor GRIP1 in macrophages.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 23;8(1):1739. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01569-2. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29170386 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection of SAK3 on scopolamine-induced cholinergic dysfunction in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.Cytotechnology. 2020 Feb;72(1):155-164. doi: 10.1007/s10616-019-00366-7. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Cytotechnology. 2020. PMID: 31933104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kellum J. A., Kong L., Fink M. P., Weissfeld L. A., Yealy D. M., Pinsky M. R., Fine J., Krichevsky A., Delude R. L., Angus D. C.; GenIMS Investigators (2007) Understanding the inflammatory cytokine response in pneumonia and sepsis: results of the Genetic and Inflammatory Markers of Sepsis (GenIMS) Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 167, 1655–1663 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. (2007) TLR signaling. Semin. Immunol. 19, 24–32 - PubMed
-
- Lee M. S., Kim Y. J. (2007) Signaling pathways downstream of pattern-recognition receptors and their cross talk. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 447–480 - PubMed
-
- O’Neill L. A. (2008) ‘Fine tuning’ TLR signaling. Nat. Immunol. 9, 459–461 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

