The interplay between TEAD4 and KLF5 promotes breast cancer partially through inhibiting the transcription of p27Kip1
- PMID: 25970772
- PMCID: PMC4627338
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3779
The interplay between TEAD4 and KLF5 promotes breast cancer partially through inhibiting the transcription of p27Kip1
Abstract
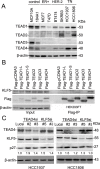
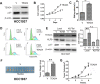
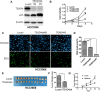
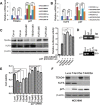
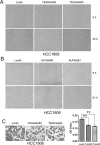
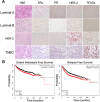
Growing evidence suggests that YAP/TAZ are mediators of the Hippo pathway and promote breast cancer. However, the roles of YAP/TAZ transcription factor partners TEADs in breast cancer remain unclear. Here we found that TEAD4 was expressed in breast cancer cell lines, especially in triple negative breast cancers (TNBC) cell lines. TEAD4 binds to KLF5. Knockdown of either TEAD4 or KLF5 in HCC1937 and HCC1806 cells induced the expression of CDK inhibitor p27. Depletion of either TEAD4 or KLF5 activated the p27 gene promoter and increased the p27 mRNA levels. Depletion of p27 partially prevents growth inhibition caused by TEAD4 and KLF5 knockdown. TEAD4 overexpression stimulated proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in mice, while stable knockdown of TEAD4 inhibited proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in mice. Thus TEAD4 and KLF5, in collaboration, promoted TNBC cell proliferation and tumor growth in part by inhibiting p27 gene transcription. TEAD4 is a potential target and biomarker for the development of novel therapeutics for breast cancer.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; KLF5; TEAD4; TNBC; p27.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kruppel-like factor 5 transcription factor promotes microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase 1 gene transcription in breast cancer.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 13;288(37):26731-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.483958. Epub 2013 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23913682 Free PMC article.
-
TEAD4-YAP interaction regulates tumoral growth by controlling cell-cycle arrest at the G1 phase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Apr 29;486(2):385-390. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.03.050. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28315328
-
YAP promotes breast cell proliferation and survival partially through stabilizing the KLF5 transcription factor.Am J Pathol. 2012 Jun;180(6):2452-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.02.025. Am J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22632819
-
Structural and Functional Overview of TEAD4 in Cancer Biology.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 6;13:9865-9874. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S266649. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33116572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TEAD4: A key regulator of tumor metastasis and chemoresistance - Mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Jan;1879(1):189050. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189050. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38072284 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of TEAD Transcription Factors in Cancer Biology.Cells. 2019 Jun 17;8(6):600. doi: 10.3390/cells8060600. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31212916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of Covalent Inhibitors Targeting the Transcriptional Enhanced Associate Domain Central Pocket.J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 22;63(20):11972-11989. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01275. Epub 2020 Oct 1. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32907324 Free PMC article.
-
Mifepristone Derivative FZU-00,003 Suppresses Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cell Growth partially via miR-153-KLF5 axis.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jan 1;16(4):611-619. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.39491. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32025209 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of an independent poor-prognosis subtype associated with tertiary lymphoid structures in breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 20;15:1364506. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1364506. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38571938 Free PMC article.
-
TEAD transcription factor family emerges as a promising therapeutic target for oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 4;15:1480701. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1480701. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39430767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pan D. Hippo signaling in organ size control. Genes & development. 2007;21:886–897. - PubMed
-
- Yin M, Zhang L. Hippo signaling: a hub of growth control, tumor suppression and pluripotency maintenance. Journal of genetics and genomics = Yi chuan xue bao. 2011;38:471–481. - PubMed
-
- Oka T, Mazack V, Sudol M. Mst2 and Lats kinases regulate apoptotic function of Yes kinase-associated protein (YAP) The Journal of biological chemistry. 2008;283:27534–27546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

