The TOPCONS web server for consensus prediction of membrane protein topology and signal peptides
- PMID: 25969446
- PMCID: PMC4489233
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv485
The TOPCONS web server for consensus prediction of membrane protein topology and signal peptides
Abstract
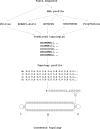
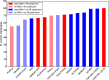
TOPCONS (http://topcons.net/) is a widely used web server for consensus prediction of membrane protein topology. We hereby present a major update to the server, with some substantial improvements, including the following: (i) TOPCONS can now efficiently separate signal peptides from transmembrane regions. (ii) The server can now differentiate more successfully between globular and membrane proteins. (iii) The server now is even slightly faster, although a much larger database is used to generate the multiple sequence alignments. For most proteins, the final prediction is produced in a matter of seconds. (iv) The user-friendly interface is retained, with the additional feature of submitting batch files and accessing the server programmatically using standard interfaces, making it thus ideal for proteome-wide analyses. Indicatively, the user can now scan the entire human proteome in a few days. (v) For proteins with homology to a known 3D structure, the homology-inferred topology is also displayed. (vi) Finally, the combination of methods currently implemented achieves an overall increase in performance by 4% as compared to the currently available best-scoring methods and TOPCONS is the only method that can identify signal peptides and still maintain a state-of-the-art performance in topology predictions.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TOPCONS: consensus prediction of membrane protein topology.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(Web Server issue):W465-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp363. Epub 2009 May 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19429891 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid membrane protein topology prediction.Bioinformatics. 2011 May 1;27(9):1322-3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr119. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21493661 Free PMC article.
-
CCTOP: a Consensus Constrained TOPology prediction web server.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 1;43(W1):W408-12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv451. Epub 2015 May 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25943549 Free PMC article.
-
Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction--the Phobius web server.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W429-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm256. Epub 2007 May 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17483518 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-assisted protein domain boundary prediction using the DomPred server.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2007 Apr;8(2):181-8. doi: 10.2174/138920307780363415. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2007. PMID: 17430199 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Characterization of GPCRs for Pyrokinin and CAPA Peptides in the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae).Front Physiol. 2020 May 29;11:559. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00559. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32547421 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic Characterization of Sulfotransferase Provides New Insights for the Exploitation of Sulfated Polysaccharides in Caulerpa.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 12;21(18):6681. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186681. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32932673 Free PMC article.
-
Using the Ubiquitin-modified Proteome to Monitor Distinct and Spatially Restricted Protein Homeostasis Dysfunction.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Aug;15(8):2576-93. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.058420. Epub 2016 May 16. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27185884 Free PMC article.
-
Phase separation modulates the assembly and dynamics of a polarity-related scaffold-signaling hub.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 23;13(1):7181. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35000-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36418326 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Sequences of the Mycobacteriophages Awesomesauce and LastJedi.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020 Aug 20;9(34):e00707-20. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00707-20. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020. PMID: 32816978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krogh A., Larsson B., von Heijne G., Sonnhammer E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001;305:567–580. - PubMed
-
- von Heijne G. The membrane protein universe: what's out there and why bother. J. Inter. Med. 2007;261:543–557. - PubMed
-
- Bakheet T.M., Doig A.J. Properties and identification of human protein drug targets. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:451–457. - PubMed
-
- Davey J. G-protein-coupled receptors: new approaches to maximise the impact of GPCRS in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2004;8:165–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

